Cardiac fibroblasts mediate IL-17A-driven inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 24935258
- PMCID: PMC4076595
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20132126
Cardiac fibroblasts mediate IL-17A-driven inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract
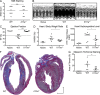
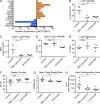
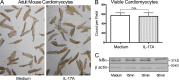
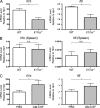
Inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMi) is a major cause of heart failure in individuals below the age of 40. We recently reported that IL-17A is required for the development of DCMi. We show a novel pathway connecting IL-17A, cardiac fibroblasts (CFs), GM-CSF, and heart-infiltrating myeloid cells with the pathogenesis of DCMi. Il17ra(-/-) mice were protected from DCMi, and this was associated with significantly diminished neutrophil and Ly6Chi monocyte/macrophage (MO/MΦ) cardiac infiltrates. Depletion of Ly6Chi MO/MΦ also protected mice from DCMi. Mechanistically, IL-17A stimulated CFs to produce key chemokines and cytokines that are critical downstream effectors in the recruitment and differentiation of myeloid cells. Moreover, IL-17A directs Ly6Chi MO/MΦ in trans toward a more proinflammatory phenotype via CF-derived GM-CSF. Collectively, this IL-17A-fibroblast-GM-CSF-MO/MΦ axis could provide a novel target for the treatment of DCMi and related inflammatory cardiac diseases.
© 2014 Wu et al.
Figures





References
-
- Aretz H.T., Billingham M.E., Edwards W.D., Factor S.M., Fallon J.T., Fenoglio J.J., Jr, Olsen E.G., Schoen F.J. 1987. Myocarditis. A histopathologic definition and classification. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 1:3–14 - PubMed
-
- Baldeviano G.C., Barin J.G., Talor M.V., Srinivasan S., Bedja D., Zheng D., Gabrielson K., Iwakura Y., Rose N.R., Cihakova D. 2010. Interleukin-17A is dispensable for myocarditis but essential for the progression to dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 106:1646–1655 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.213157 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

