Effects of schizophrenia risk variation in the NRG1 gene on NRG1-IV splicing during fetal and early postnatal human neocortical development
- PMID: 24935406
- PMCID: PMC4330971
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.13111518
Effects of schizophrenia risk variation in the NRG1 gene on NRG1-IV splicing during fetal and early postnatal human neocortical development
Abstract
Objective: Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) is a multifunctional neurotrophin that mediates neurodevelopment and schizophrenia risk. The NRG1 gene undergoes extensive alternative splicing, and association of brain NRG1 type IV isoform expression with the schizophrenia-risk polymorphism rs6994992 is a potential mechanism of risk. Novel splice variants of NRG1-IV (NRG1-IVNV), with predicted unique signaling capabilities, have been cloned in fetal brain tissue. The authors investigated the temporal dynamics of transcription of NRG1-IVNV, compared with the major NRG1 isoforms, across human prenatal and postnatal prefrontal cortical development, and they examined the association of rs6994992 with NRG1-IVNV expression.
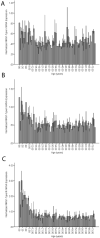
Method: NRG1 type I-IV and NRG1-IVNV isoforms were evaluated with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in human postmortem prefrontal cortex tissue samples at 14 to 39 weeks gestation and postnatal ages 0-83 years. The association of rs6994992 genotype with NRG1-IVNV expression and the subcellular distribution and proteolytic processing of NRG1-IVNV isoforms were also determined.
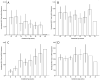
Results: Expression of NRG1 types I, II, and III was temporally regulated during prenatal and postnatal neocortical development. NRG1-IVNV was expressed from 16 weeks gestation until age 3. Homozygosity for the schizophrenia risk allele (T) of rs6994992 conferred lower cortical NRG1-IVNV levels. Assays showed that NRG1-IVNV is a novel nuclear-enriched, truncated NRG1 protein resistant to proteolytic processing.
Conclusions: To the authors' knowledge, this study provides the first quantitative map of NRG1 isoform expression during human neocortical development and aging. It identifies a potential mechanism of early developmental risk for schizophrenia at the NRG1 locus, involving a novel class of NRG1 proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Paterson, Wang, Kleinman and Law report no competing interests.
Figures
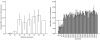
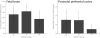

Comment in
-
Identifying pathways leading to prefrontal GABA-ergic interneuron dysfunction in schizophrenia.Am J Psychiatry. 2014 Sep;171(9):906-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14060750. Am J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25178745 No abstract available.
References
-
- Falls DL. Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:14–30. - PubMed
-
- Steinthorsdottir V, Stefansson H, Ghosh S, Birgisdottir B, Bjornsdottir S, Fasquel AC, Olafsson O, Stefansson K, Gulcher JR. Multiple novel transcription initiation sites for NRG1. Gene. 2004;342:97–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

