Emotion differentiation and alcohol-related problems: the mediating role of urgency
- PMID: 24935796
- PMCID: PMC4102173
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.05.004
Emotion differentiation and alcohol-related problems: the mediating role of urgency
Abstract
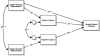
Deficits in emotional and behavioral regulation figure prominently in etiological models of alcohol-related problems. This study tests a model linking poor differentiation of emotion to alcohol-related problems via urgency. The sample consisted of 102 undergraduates between the ages 18 and 24 who reported moderate to heavy alcohol consumption. As hypothesized, negative urgency mediated the relationship between negative emotion differentiation and alcohol-related problems. However, contrary to hypothesis, positive urgency was not associated with either positive emotion differentiation or alcohol-related problems and the indirect effect of positive emotion differentiation via positive urgency was not significant. Instead, positive emotion differentiation exhibited a significant direct effect on alcohol-related problems. This study provides an initial examination of connections between specificity in labeling emotions, behavioral disinhibition, and problematic alcohol use. These findings suggest that poor differentiation of negative emotion may foster impulsive behavior when negatively aroused. Whereas, impulsive behavior when positively aroused may reflect heightened sensitivity to positive reinforcement, which may not be related to reflective processes underlying emotion differentiation.
Keywords: Alcohol; Alcohol-related problems; Emotion; Emotion differentiation; Urgency.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Csikszentmihalyi M, Larson R. Validity and reliability of the Experience Sampling Method. In: deVries MW, editor. The experience of psychopathology: Investigating mental disorders in their natural settings. New York, NY US: Cambridge University Press; 1992. pp. 43–57.
-
- Cyders MA, Smith GT. Mood-based rash action and its components: Positive and negative urgency. Personality & Individual Differences. 2007;43(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2007.02.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials