Detection of Bartonella quintana in African body and head lice
- PMID: 24935950
- PMCID: PMC4125252
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0707
Detection of Bartonella quintana in African body and head lice
Abstract
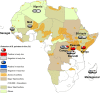
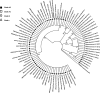
Currently, the body louse is the only recognized vector of Bartonella quintana, an organism that causes trench fever. In this work, we investigated the prevalence of this bacterium in human lice in different African countries. We tested 616 head lice and 424 body lice from nine African countries using real-time polymerase chain reaction targeting intergenic spacer region 2 and specific B. quintana genes. Overall, B. quintana DNA was found in 54% and 2% of body and head lice, respectively. Our results also show that there are more body lice positive for B. quintana in poor countries, which was determined by the gross domestic product, than in wealthy areas (228/403 versus 0/21, P < 0.001). A similar finding was obtained for head lice (8/226 versus 2/390, P = 0.007). Our findings suggest that head lice in Africa may be infected by B. quintana when patients live in poor economic conditions and are also exposed to body lice.
© The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Figures

References
-
- Barker SC. Phylogeny and classification, origins, and evolution of host associations of lice. Int J Parasitol. 1994;24:1285–1291. - PubMed
-
- Light JE, Toups MA, Reed DL. What's in a name: the taxonomic status of human head and body lice. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008;47:1203–1216. - PubMed
-
- Badiaga S, Brouqui P. Human louse-transmitted infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:332–337. - PubMed
-
- Nuttall GHF. The biology of Pediculus humanus. Parasitology. 1917;10:80–185.
-
- Busvine JR. Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 1946. On the pigmentation of the body louse pediculus humanus L. In Proceedings of the Royal Entomological Society of London. Series A, General Entomology (Vol. 21, No. 10--12, pp. 98--103)
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

