Dichotomous branching: the plant form and integrity upon the apical meristem bifurcation
- PMID: 24936206
- PMCID: PMC4047680
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00263
Dichotomous branching: the plant form and integrity upon the apical meristem bifurcation
Abstract
The division of the apical meristem into two independently functioning axes is defined as dichotomous branching. This type of branching typically occurs in non-vascular and non-seed vascular plants, whereas in seed plants it presents a primary growth form only in several taxa. Dichotomy is a complex process, which requires a re-organization of the meristem structure and causes changes in the apex geometry and activity. However, the mechanisms governing the repetitive apex divisions are hardly known. Here, an overview of dichotomous branching is presented, occurring in structurally different apices of phylogenetically distant plants, and in various organs (e.g., shoots, roots, rhizophores). Additionally, morphogenetic effects of dichotomy are reviewed, including its impact on organogenesis and mechanical constraints. At the end, the hormonal and genetic regulation of the dichotomous branching is discussed.
Keywords: apical cell; apical meristems; dichotomy; meristem bifurcation; terminal branching.
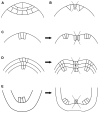
Figures
References
-
- Ahern C. P., Staff I. A. (1994). Symbiosis in cycads: the origin and development of coralloid root in Macrozamia communis (Cycadaceae). Am. J. Bot. 81 1559–1570 10.2307/2445333 - DOI
-
- Barlow P. W. (1992). From cell wall networks to algorithms. The simulation and cytology of cell division patterns in plants. Protoplasma 162 69–85 10.1007/BF02562551 - DOI
-
- Bierhorst D. W. (1977). On the stem apex, leaf initiation and early leaf ontogeny in filicalean ferns. Am. J. Bot. 64125–152 10.2307/2442101 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

