Adrenomedullin and diabetes
- PMID: 24936257
- PMCID: PMC4058740
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i3.364
Adrenomedullin and diabetes
Abstract
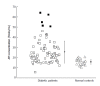
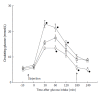
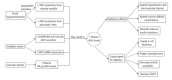
Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a peptide hormone widely expressed in different tissues, especially in the vasculature. Apart from its vasodilatatory and hypotensive effect, it plays multiple roles in the regulation of hormonal secretion, glucose metabolism and inflammatory response. ADM regulates insulin balance and may participate in the development of diabetes. The plasma level of ADM is increased in people with diabetes, while in healthy individuals the plasma ADM concentration remains low. Plasma ADM levels are further increased in patients with diabetic complications. In type 1 diabetes, plasma ADM level is correlated with renal failure and retinopathy, while in type 2 diabetes its level is linked with a wider range of complications. The elevation of ADM level in diabetes may be due to hyperinsulinemia, oxidative stress and endothelial injury. At the same time, a rise in plasma ADM level can trigger the onset of diabetes. Strategies to reduce ADM level should be explored so as to reduce diabetic complications.
Keywords: Adrenomedullin; Diabetes; Diabetic complications; Hyperglycemia; Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Hayashi M, Shimosawa T, Isaka M, Yamada S, Fujita R, Fujita T. Plasma adrenomedullin in diabetes. Lancet. 1997;350:1449–1450. - PubMed
-
- Martínez A, Weaver C, López J, Bhathena SJ, Elsasser TH, Miller MJ, Moody TW, Unsworth EJ, Cuttitta F. Regulation of insulin secretion and blood glucose metabolism by adrenomedullin. Endocrinology. 1996;137:2626–2632. - PubMed
-
- Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H, Eto T. Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:553–560. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

