Emerging role of protein kinase C in energy homeostasis: A brief overview
- PMID: 24936260
- PMCID: PMC4058743
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i3.385
Emerging role of protein kinase C in energy homeostasis: A brief overview
Abstract
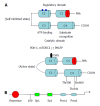
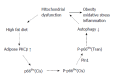
Protein kinase C-β (PKCβ), a member of the lipid-activated serine/threonine PKC family, has been implicated in a wide range of important cellular processes. Very recently, the novel role of PKCβ in the regulation of triglyceride homeostasis via regulating mitochondrial function has been explored. In this review, I aim to provide an overview of PKCβ regarding regulation by lipids and recently gained knowledge on its role in energy homeostasis. Alterations in adipose PKCβ expression have been shown to be crucial for diet-induced obesity and related metabolic abnormalities. High-fat diet is shown to induce PKCβ expression in white adipose tissue in an isoform- and tissue-specific manner. Genetically manipulated mice devoid of PKCβ are lean with increased oxygen consumption and are resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis with improved insulin sensitivity. Available data support the model in which PKCβ functions as a "diet-sensitive" metabolic sensor whose induction in adipose tissue by high-fat diet is among the initiating event disrupting mitochondrial homeostasis via intersecting with p66(Shc) signaling to amplify adipose dysfunction and have systemic consequences. Alterations in PKCβ expression and/or function may have important implications in health and disease and warrants a detailed investigation into the downstream target genes and the underlying mechanisms involved. Development of drugs that target the PKCβ pathway and identification of miRs specifically controlling PKCβ expression may lead to novel therapeutic options for treating age-related metabolic disease including fatty liver, obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: High-fat diet; Insulin resistance; Mitochondrial function; Obesity; Signal transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C-beta: An emerging connection between nutrient excess and obesity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1841(10):1491-1497. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25064690 Review.
-
Modulation of Hepatic Protein Kinase Cβ Expression in Metabolic Adaptation to a Lithogenic Diet.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Jun 3;1(4):395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.05.008. eCollection 2015 Jul. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 28210689 Free PMC article.
-
PKCβ: Expanding role in hepatic adaptation of cholesterol homeostasis to dietary fat/cholesterol.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;312(3):G266-G273. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00373.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28104587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gdf11 gene transfer prevents high fat diet-induced obesity and improves metabolic homeostasis in obese and STZ-induced diabetic mice.J Transl Med. 2019 Dec 17;17(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-02166-1. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31847906 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase Cβ deficiency attenuates obesity syndrome of ob/ob mice by promoting white adipose tissue remodeling.J Lipid Res. 2012 Mar;53(3):368-378. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M019687. Epub 2011 Dec 30. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22210924 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial remodeling in mice with cardiomyocyte-specific lipid overload.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015 Feb;79:275-83. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.12.001. Epub 2014 Dec 9. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25497302 Free PMC article.
-
Diacylglycerol-evoked activation of PKC and PKD isoforms in regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism: a review.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 May 28;19(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01286-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32466765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of beige-like adipocyte markers and functions in 3T3-L1 cells by Clk1 and PKCβII inhibitory molecules.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Aug;26(15):4183-4194. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17345. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35801494 Free PMC article.
-
PKCβII-induced upregulation of PGP9.5 and VEGF in postoperative persistent pain in rats.J Pain Res. 2018 Sep 27;11:2095-2106. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S144852. eCollection 2018. J Pain Res. 2018. PMID: 30310311 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cellular senescence-related genes as biomarkers for lupus nephritis based on bioinformatics.Front Genet. 2025 Apr 11;16:1551450. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1551450. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40290492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parker PJ. Protein kinase C: a structurally related family of enzymes Protein kinase C: current concepts and future perspectives. Epand RM, Lester DS, editors. Ellis Horwood: 1992. pp. 3–24.
-
- Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular responses. FASEB J. 1995;9:484–496. - PubMed
-
- Newton AC. Protein kinase C: structure, function, and regulation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:28495–28498. - PubMed
-
- Ono Y, Kikkawa U, Ogita K, Fujii T, Kurokawa T, Asaoka Y, Sekiguchi K, Ase K, Igarashi K, Nishizuka Y. Expression and properties of two types of protein kinase C: alternative splicing from a single gene. Science. 1987;236:1116–1120. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

