Vitamin k dependent proteins and the role of vitamin k2 in the modulation of vascular calcification: a review
- PMID: 24936265
- PMCID: PMC4052396
- DOI: 10.5001/omj.2014.44
Vitamin k dependent proteins and the role of vitamin k2 in the modulation of vascular calcification: a review
Abstract
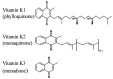
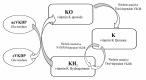
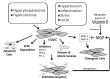
Vascular calcification, a cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, is an actively regulated process involving vitamin K dependent proteins (VKDPs) among others. Vitamin K is an essential micronutrient, present in plants and animal fermented products that plays an important role as a cofactor for the post-translational γ-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues in a number of proteins. These VKDPs require carboxylation to become biologically active, and they have been identified as having an active role in vascular cell migration, angiogenesis and vascular calcification. This paper will review the process of vascular calcification and delineate the role that vitamin K2 plays in the modulation of that process, through the activation of VKDPs. One such VKDP is Matrix Gla Protein (MGP), which when activated inhibits osteogenic factors, thereby inhibiting vascular and soft tissue calcification.
Keywords: Matrix glutamate-Protein (MGP); Menaquinone; Vascular Calcification; Vitamin K; Vitamin K antagonists; Vitamin K2; Warfarin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vitamin K-dependent proteins, warfarin, and vascular calcification.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Sep;3(5):1504-10. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00770208. Epub 2008 May 21. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18495950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K, bone fractures, and vascular calcifications in chronic kidney disease: an important but poorly studied relationship.J Endocrinol Invest. 2011 Apr;34(4):317-23. doi: 10.1007/BF03347093. Epub 2010 Nov 16. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011. PMID: 21088475 Review.
-
[Vitamin K, bone metabolism and vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease].Przegl Lek. 2011;68(9):629-32. Przegl Lek. 2011. PMID: 22335014 Review. Polish.
-
The Inhibitory Roles of Vitamin K in Progression of Vascular Calcification.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 23;12(2):583. doi: 10.3390/nu12020583. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32102248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of vitamin K and vitamin K-dependent proteins in vascular calcification.Z Kardiol. 2001;90 Suppl 3:57-63. doi: 10.1007/s003920170043. Z Kardiol. 2001. PMID: 11374034
Cited by
-
The Complex Interplay of Inflammation, Metabolism, Epigenetics, and Sex in Calcific Disease of the Aortic Valve.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jan 6;8:791646. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.791646. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35071359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plausible ergogenic effects of vitamin D on athletic performance and recovery.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Aug 19;12:33. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0093-8. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26288575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Vitamin K Status on Glycemic Regulation and Diabetes Mellitus: A Mini-Review.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 18;12(8):2485. doi: 10.3390/nu12082485. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32824773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Medical Benefits of Vitamin K2 on Calcium-Related Disorders.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 21;13(2):691. doi: 10.3390/nu13020691. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33670005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Vitamin K2 (Menaquionones) in Children's Health and Diseases: A Review of the Literature.Children (Basel). 2022 Jan 5;9(1):78. doi: 10.3390/children9010078. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
