Biological effects and equivalent doses in radiotherapy: A software solution
- PMID: 24936319
- PMCID: PMC4055002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2013.08.004
Biological effects and equivalent doses in radiotherapy: A software solution
Abstract
Background: The limits of TDF (time, dose, and fractionation) and linear quadratic models have been known for a long time. Medical physicists and physicians are required to provide fast and reliable interpretations regarding delivered doses or any future prescriptions relating to treatment changes.
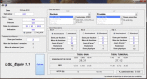
Aim: We, therefore, propose a calculation interface under the GNU license to be used for equivalent doses, biological doses, and normal tumor complication probability (Lyman model).
Materials and methods: THE METHODOLOGY USED DRAWS FROM SEVERAL SOURCES: the linear-quadratic-linear model of Astrahan, the repopulation effects of Dale, and the prediction of multi-fractionated treatments of Thames.
Results and conclusions: The results are obtained from an algorithm that minimizes an ad-hoc cost function, and then compared to an equivalent dose computed using standard calculators in seven French radiotherapy centers.
Keywords: Fractionation; Linear quadratic; Radiobiology; Repopulation; Time effect.
Figures
References
-
- Spotheim-Maurizot M., Mostafavi M., Belloni J., Douki T. EDP Sciences; L’Editeur: 2008. Radiation chemistry: from basics to applications in material and life sciences.
-
- Deutsch E., Vozenin M.C. La radiobiologie, une discipline d’interface. Cancer/Radiothérapie. 2011;15(5):347. - PubMed
-
- Steel G.G. 3rd Revised edition. Hodder Arnold; 2002. Basic clinical radiobiology.
-
- Joubert A., Vogin G., Devic C. Biologie des radiations: avancées majeures et perspectives pour la radiothérapie. Cancer/Radiothérapie. 2011;15(5):348–354. - PubMed
-
- Foray N. Aspects radiobiologiques des traitements anticancéreux par rayonnement synchrotron: bilan et perspectives. Cancer/Radiothérapie. 2010;14(2):145–154. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources