Genetic and chemical correction of cholesterol accumulation and impaired autophagy in hepatic and neural cells derived from Niemann-Pick Type C patient-specific iPS cells
- PMID: 24936472
- PMCID: PMC4050353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.03.014
Genetic and chemical correction of cholesterol accumulation and impaired autophagy in hepatic and neural cells derived from Niemann-Pick Type C patient-specific iPS cells
Abstract
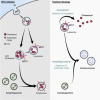
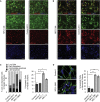
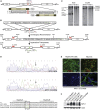
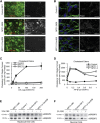
Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease is a fatal inherited lipid storage disorder causing severe neurodegeneration and liver dysfunction with only limited treatment options for patients. Loss of NPC1 function causes defects in cholesterol metabolism and has recently been implicated in deregulation of autophagy. Here, we report the generation of isogenic pairs of NPC patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) using transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs). We observed decreased cell viability, cholesterol accumulation, and dysfunctional autophagic flux in NPC1-deficient human hepatic and neural cells. Genetic correction of a disease-causing mutation rescued these defects and directly linked NPC1 protein function to impaired cholesterol metabolism and autophagy. Screening for autophagy-inducing compounds in disease-affected human cells showed cell type specificity. Carbamazepine was found to be cytoprotective and effective in restoring the autophagy defects in both NPC1-deficient hepatic and neuronal cells and therefore may be a promising treatment option with overall benefit for NPC disease.
Figures


References
-
- Bjørkøy G., Lamark T., Pankiv S., Øvervatn A., Brech A., Johansen T. Monitoring autophagic degradation of p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 2009;452:181–197. - PubMed
-
- Brown M.S., Goldstein J.L. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Carstea E.D., Morris J.A., Coleman K.G., Loftus S.K., Zhang D., Cummings C., Gu J., Rosenfeld M.A., Pavan W.J., Krizman D.B. Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1997;277:228–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

