A rare sequence variant in intron 1 of THAP1 is associated with primary dystonia
- PMID: 24936516
- PMCID: PMC4049367
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.67
A rare sequence variant in intron 1 of THAP1 is associated with primary dystonia
Abstract
Although coding variants in THAP1 have been causally associated with primary dystonia, the contribution of noncoding variants remains uncertain. Herein, we examine a previously identified Intron 1 variant (c.71+9C>A, rs200209986). Among 1672 subjects with mainly adult-onset primary dystonia, 12 harbored the variant in contrast to 1/1574 controls (P < 0.01). Dystonia classification included cervical dystonia (N = 3), laryngeal dystonia (adductor subtype, N = 3), jaw-opening oromandibular dystonia (N = 1), blepharospasm (N = 2), and unclassified (N = 3). Age of dystonia onset ranged from 25 to 69 years (mean = 54 years). In comparison to controls with no identified THAP1 sequence variants, the c.71+9C>A variant was associated with an elevated ratio of Isoform 1 (NM_018105) to Isoform 2 (NM_199003) in leukocytes. In silico and minigene analyses indicated that c.71+9C>A alters THAP1 splicing. Lymphoblastoid cells harboring the c.71+9C>A variant showed extensive apoptosis with relatively fewer cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. Differentially expressed genes from lymphoblastoid cells revealed that the c.71+9C>A variant exerts effects on DNA synthesis, cell growth and proliferation, cell survival, and cytotoxicity. In aggregate, these data indicate that THAP1 c.71+9C>A is a risk factor for adult-onset primary dystonia.
Keywords: DYT6; Dystonia; THAP1; intronic variant; minigene assay.
Figures
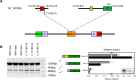
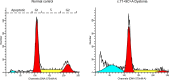
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate – a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Blanchard DA, Mouhamad S, Auffredou MT, Pesty A, Bertoglio J, Leca G, et al. Cdk2 associates with MAP kinase in vivo and its nuclear translocation is dependent on MAP kinase activation in IL-2-dependent Kit 225 T lymphocytes. Oncogene. 2000;19:4184–4189. - PubMed
-
- Brunak S, Engelbrecht J, Knudsen S. Prediction of human mRNA donor and acceptor sites from the DNA sequence. J. Mol. Biol. 1991;220:49–65. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

