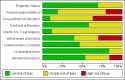
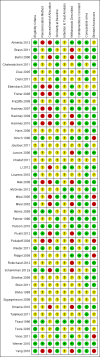
Physiotherapy for Parkinson's disease: a comparison of techniques
- PMID: 24936965
- PMCID: PMC7120367
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002815.pub2
Physiotherapy for Parkinson's disease: a comparison of techniques
Abstract
Background: Despite medical therapies and surgical interventions for Parkinson's disease (PD), patients develop progressive disability. The role of physiotherapy is to maximise functional ability and minimise secondary complications through movement rehabilitation within a context of education and support for the whole person. The overall aim is to optimise independence, safety and wellbeing, thereby enhancing quality of life. Trials have shown that physiotherapy has short-term benefits in PD. However, which physiotherapy intervention is most effective remains unclear.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of one physiotherapy intervention compared with a second approach in patients with PD.
Search methods: Relevant trials were identified by electronic searches of numerous literature databases (for example MEDLINE, EMBASE) and trial registers, plus handsearching of major journals, abstract books, conference proceedings and reference lists of retrieved publications. The literature search included trials published up to the end of January 2012.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials of one physiotherapy intervention versus another physiotherapy intervention in patients with PD.
Data collection and analysis: Data were abstracted independently from each paper by two authors. Trials were classified into the following intervention comparisons: general physiotherapy, exercise, treadmill training, cueing, dance and martial arts.
Main results: A total of 43 trials were identified with 1673 participants. All trials used small patient numbers (average trial size of 39 participants); the methods of randomisation and concealment of allocation were poor or not stated in most trials. Blinded assessors were used in just over half of the trials and only 10 stated that they used intention-to-treat analysis.A wide variety of validated and customised outcome measures were used to assess the effectiveness of physiotherapy interventions. The most frequently reported physiotherapy outcomes were gait speed and timed up and go, in 19 and 15 trials respectively. Only five of the 43 trials reported data on falls (12%). The motor subscales of the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale and Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire-39 were the most commonly reported clinician-rated disability and patient-rated quality of life outcome measures, used in 22 and 13 trials respectively. The content and delivery of the physiotherapy interventions varied widely in the trials included within this review, so no quantitative meta-analysis could be performed.
Authors' conclusions: Considering the small number of participants examined, the methodological flaws in many of the studies, the possibility of publication bias, and the variety of interventions, formal comparison of the different physiotherapy techniques could not be performed. There is insufficient evidence to support or refute the effectiveness of one physiotherapy intervention over another in PD.This review shows that a wide range of physiotherapy interventions to treat PD have been tested . There is a need for more specific trials with improved treatment strategies to underpin the most appropriate choice of physiotherapy intervention and the outcomes measured.
Conflict of interest statement
Carl Clarke, Natalie Ives, Charmaine Meek, Smitaa Patel, Catherine Sackley and Keith Wheatley are either recruiting for or involved in the running of the UK PD REHAB trial.
Figures
Update of
-
A comparison of physiotherapy techniques for patients with Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD002815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002815. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 17;(6):CD002815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002815.pub2. PMID: 11279765 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Almeida 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Braun 2011 {published data only}
-
- Braun S, Beurskens A, Kleynen M, Schols J, Wade D. Rehabilitation with mental practice has similar effects on mobility as rehabilitation with relaxation in people with Parkinson's disease: a multicentre randomised trial. Journal of Physiotherapy 2011;57(1):27‐34. - PubMed
Burini 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Burini D, Farabollini B, Iacucci S, Rimatori C, Riccardi G, Capecci M, et al. A randomised controlled cross‐over trial of aerobic training versus Qigong in advanced Parkinson's disease. Europa Medicophysica 2006;42(3):231‐8. - PubMed
Chaiwanichsiri 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chaiwanichsiri D. Treadmill and music cueing for gait training in mild to moderate Parkinson's disease. clinicaltrials.gov 2009.
-
- Chaiwanichsiri D, Wangno W, Kitisomprayoonkul W, Bhidayasiri R. Treadmill training with music cueing: a new approach for Parkinson's gait facilitation. Asian Biomedicine 2011;5(5):649‐54.
Dias 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dias NP, Fraga DA, Cacho EWA, Oberg TD. Training of gait with visual cues in the patient with Parkinson's disease. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2005;18(4):43‐51.
Diehl 2011 {published data only}
-
- Diehl D, Combs S, Staples B. Comparison of boxing training and traditional exercise on balance and quality of life outcomes in persons with Parkinson's disease: a pilot study. Movement Disorders 2011;26:S124.
Ebersbach 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ebersbach G, Ebersbach A, Edler D, Kaufhold O, Kusch M, Kupsch A, et al. Comparing exercise in Parkinson's disease ‐ The Berlin LSVT (R) BIG study. Movement Disorders 2010;25(12):1902‐8. - PubMed
Fisher 2008 {published data only}
Frazzitta 2009 {published data only}
-
- Frazzitta G, Maestri R, Uccellini D, Bertotti G, Abelli P. Rehabilitation treatment of gait in patients with Parkinson's disease with freezing: A comparison between two physical therapy protocols using visual and auditory cues with or without treadmill training. Movement Disorders 2009;24(8):1139‐43. - PubMed
Hackney 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hackney ME, Kantorovich S, Levin R, Earhart GM. Effects of tango on functional mobility in Parkinson's disease: A preliminary study. Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy 2007;31(4):173‐9. - PubMed
Hackney 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Hackney 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Hass 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hass CJ, Waddell DE, Wolf SL, Juncos JL, Gregor RJ. The influence of tai chi training on locomotor ability in Parkinson's disease. American Society of Biomechanics (www.asbweb.org/conferences/2006/pdfs/154.pdf). 2006:154.
Hirsch 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hirsch MA. Activity dependent enhancement of balance following strength and balance training. PhD Thesis, Florida State University 1996. [UMI Number: 9622856]
-
- Hirsch MA, Toole T, Maitland CG, Rider RA. The effects of balance training and high‐intensity resistance training on persons with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2003;84(8):1109‐17. - PubMed
Joudoux 2011 {published data only}
-
- Joudoux S, Santiago T, Hutin E, Bayle N, Gracies JM. Randomised controlled single‐blind trial comparing two rehabilitation programs in Parkinson's disease at a moderate stage: Methodology. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. Conference proceeding 2011;54:e104.
Juncos 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Juncos JL. Chinese exercise modalities in Parkinson's disease. controlled‐trials.com 2010.
-
- Juncos JL, Haber M, Waddell D, Gregor R, Wohl SL. A controlled study of aerobic exercise and Chinese exercise modalities in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2006;66(5 Suppl 2):A314.
Khallaf 2011 {published data only}
-
- Khallaf MES, Fathy H. Influence of moderate aerobic exercises on activities of daily living and depression in patients with Parkinson's disease. European Journal of Neurology. Conference proceeding 2011;18:439.
Li 2012 {published data only}
-
- Li F, Fitzgerald K. Postural stability in Parkinson's disease patients after Tai Chi training: A randomised controlled trial. WFN XIX World Congress on Parkinson's Disease and Related Disorders. 2012; Vol. 18:s155.
-
- Sieber B, Fuzhong L. Tai Chi and Parkinson's disease. Report Database 2008.
Loureiro 2010 {published data only}
-
- Loureiro APC, Stori FR, Chen R, Ribas CG, Loureiro CC. Comparative study of conventional physiotherapy and virtual rehabilitation using Wii Fit for improvement of balance in Parkinson's disease patients. Movement Disorders 2010; Vol. 25 Suppl 3:S714.
Mak 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mak MK, Hui‐Chan CW. Effect of 4‐week training with audio‐visual cues on sit‐to‐stand in Parkinsonian patients. Movement Disorders 2005;20 Suppl 10:388.
-
- Mak MKY, Hui‐Chan CWY. Cued task‐specific training is better than exercise in improving sit‐to‐stand in patients with Parkinson's disease: A randomized controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2008;23(4):501‐9. - PubMed
McGinley 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Miyai 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Miyai I, Fujimoto Y, Ueda Y, Yamamoto H, Nozaki S, Saito T, et al. Treadmill training with body weight support: Its effect on Parkinson's disease. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2000;81(7):849‐52. - PubMed
Miyai 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Miyai I, Fujimoto Y, Yamamoto H, Ueda Y, Saito T, Nozaki S, et al. Long‐term effect of body weight‐supported treadmill training in Parkinson's disease: A randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2002;83(10):1370‐3. - PubMed
Morris 2009 {published data only}
-
- Martin CL, Morris ME, Iansek R. Carry‐over effects of inpatient rehabilitation in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2008;23 Suppl 1:675.
-
- Morris ME, Iansek R. Effects of strategy training compared to exercises for gait rehabilitation in Parkinson disease: A randomized controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2006;21:688.
-
- Morris ME, Iansek R, Kirkwood B. A randomized controlled trial of movement strategies compared with exercise for people with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24(1):64‐71. - PubMed
-
- Morris ME, Iansek R, Kirkwood B, Danoudis M, Martin CL. Carry‐over effects of movement strategy training in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24 Suppl 1:S270.
-
- Schenkman M. Reply: A randomized controlled trial of movement strategies compared with exercise for people with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25(4):524. - PubMed
Palmer 1986 {published data only}
-
- Palmer SS, Mortimer JA, Webster DD, Bistevins R, Dickinson GL. Comparison of stretch exercises and karate training as therapy for Parkinson's disease. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1984;65(10):626. - PubMed
-
- Palmer SS, Mortimer JA, Webster DD, Bistevins R, Dickinson GL. Exercise therapy for Parkinson's disease. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1986;67(10):741‐5. - PubMed
Pelosin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Pelosin E, Avanzino L, Bove M, Stramesi P, Nieuwboer A, Abbruzzese G. Action observation improves freezing of gait in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2010;24(8):746‐52. - PubMed
Picelli 2012 {published data only}
-
- Picelli A, Melotti C, Origano F, Waldner A, Fiaschi A, Santilli V, et al. Robot‐assisted gait training in patients with Parkinson's disease: A randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2012;26(4):353‐61. - PubMed
Poliakoff 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Poliakoff E, Galpin A, McDonald K, Dick J, Kellett M, Hayes S, et al. The effect of gym training on multiple outcomes in Parkinson's disease: A pilot randomised waiting‐list controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2009;24 Suppl 1:S374. - PubMed
Reuter 2011 {published data only}
Ridgel 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ridgel AL, Vitek JL, Alberts JL. Forced, not voluntary, exercise improves motor function in Parkinson's disease patients. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2009;23(6):600‐8. - PubMed
Robichaud 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chen D, Corcos DM. Motor deficits ‐ Experimental and clinical correlates. Report Database 2009.
-
- Corcos D, Robichaud JA, David FJ, Vaillancourt DE, Poon C, Rafferty M, et al. 24 months of exercise improves the motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 2012;78:S02.003.
-
- Rafferty MR, Robichaud JA, David FJ, Poon C, Vaillancourt DE, Comella CL, et al. Long‐term exercise improves and maintains physical function in people with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2012;27 Suppl 1:S135.
-
- Robichaud JA, Corcos D. The effect of exercise on individuals with Parkinson's disease. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
-
- Robichaud JA, Corcos D. The effect of exercise on individuals with Parkinson's disease. controlled‐trials.gov 2009.
Schenkman 2012a {published data only}
-
- Schenkman M, Shinowara N. Exercise, physical function and Parkinson's disease. Report Database 2009.
-
- Shinowara N. Gait and step training to prevent fall in Parkinson's disease. Report Database 2009.
Shankar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shankar A, Labelle N, Derwent L, Bonfield S, Eliasziw M, Hu B, et al. Treadmill‐walking with music shows a synergistic improvement in gait and balance in patients with Parkinson's disease: A randomized controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2009;24 Suppl 1:S281‐2.
Shen 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shen X, Mak MKY. Effects of 12‐week strategy‐focused balance training on balance performance and balance confidence in patients with Parkinson's disease. Hong Kong Physiotherapy Journal 2011;29(2):100.
Shiba 1999 {published data only}
-
- Shiba Y, Obuchi S, Toshima H, Yamakita H. Comparison between visual and auditory stimulation in gait training of patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. World Congress of Physical Therapy Conference. 1999.
Sigurgeirsson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sigurgeirsson AT, Bjarnadottir OH, Thorsteinsdottir MH, Ingvarsson PE. The effect of high‐volume walking with visual cues on gait in Parkinson's patients. A randomised controlled trial. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2009; Vol. 15 Suppl 2:S192.
Smania 2010 {published data only}
-
- Smania N, Corato E, Tinazzi M, Stanzani C, Fiaschi A, Girardi P, et al. Effect of balance training on postural instability in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2010;24(9):826‐34. - PubMed
Talakkad 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gupta A, Ganesan M, Pal P, Talakkad S. Effect of partial weight‐supported treadmill gait training on balance in patients with Parkinson disease. 2011 Annual Assembly of the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2011; Vol. 3, issue 10:S163‐4.
-
- Talakkad S, Ganesan M, Gupta A, Pal PK, Trichur R. Effect of partial weight supported treadmill gait training on cardiovascular dynamics in patients with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2011;26 Suppl 2:s173.
Thaut 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Thaut MH, McIntosh GC, Rice RR, Miller RA, Rathbun J, Brault JM. Rhythmic auditory stimulation in gait training for Parkinson's disease patients. Movement Disorders 1996;11(2):193‐200. - PubMed
Toole 2005 {published data only}
-
- Maitland CG, Toole T, Warren E, Hubmann MF. The effects of loading and unloading on gait and balance control in Parkinsonism. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2004;85:E13.
-
- Toole T, Maitland CG, Warren E, Hubmann MF, Panton L. The effects of loading and unloading treadmill walking on balance, gait, fall risk, and daily function in Parkinsonism. NeuroRehabilitation 2005;20(4):307‐22. - PubMed
Vivas 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vivas J, Arias P, Cudeiro J. Aquatic therapy versus conventional land‐based therapy for Parkinson's disease: an open‐label pilot study. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2011;92(8):1202‐10. - PubMed
Werner 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Werner WG, Gentile AM. Improving gait and promoting retention in individuals with Parkinson's disease: a pilot study. Journal of Neurology 2010;257(11):1841‐7. - PubMed
Yang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yang YR, Lee YY, Cheng SJ, Wang RY. Downhill walking training in individuals with Parkinson's disease: A randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2010;89(9):706‐14. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Byl 2009 {published data only}
-
- Byl N. Enhancing safe mobility in patients with Parkinson's disease: effect of dual task training during aerobic and moderate exercise. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2009;15 Suppl 2:S122.
Cheon 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cheon SM, Sung HR, Chae BK, Kim JW. Effects of different exercises in the patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2012;18:s154.
Chouza 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chouza M, Arias P, Vinas S, Cudeiro J. Acute effects of whole‐body vibration at 3, 6, and 9 hz on balance and gait in patients with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2011;26:920‐1. - PubMed
Cianci 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cianci H, Robinson K, Bunting‐Perry L, Sollenberger J, Nooregian J, Duda J. Are wheeled walkers with visual cues efficacious to treat freezing of gait in Parkinson's disease?. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2010; Vol. 16 Suppl 1:S64.
Donovan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Donovan S, Lim C, Diaz N, Browner N, Rose P, Sudarsky LR, et al. Laserlight cues for gait freezing in Parkinson's disease: An open‐label study. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2011;17(4):240‐5. - PubMed
Farley 2005 {published data only}
-
- Farley BG, Koshland GF. Learning Big (TM): Efficacy of a large‐amplitude exercise approach for patients with Parkinson's disease‐bradykinesia to balance. Movement Disorders 2005;20 Suppl 10:466.
Filippin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Filippin NT, Costa PHL, Mattioli R. Effects of treadmill‐walking training with additional body load on quality of life in subjects with Parkinson's disease. Revista Brasileira de Fisioterapia 2010;14(4):344‐50. - PubMed
Frazzitta 2012 {published data only}
-
- Frazzitta G, Bertotti G, Riboldazzi G, Turla M, Uccellini D, Boveri N, et al. A new approach to rehabilitation of Parkinsonian patients: The intensive rehabilitation treatment. Movement Disorders 2011;26:s127.
-
- Frazzitta G, Bertotti G, Riboldazzi G, Turla M, Uccellini D, Boveri N, et al. Effectiveness of intensive inpatient rehabilitation treatment on disease progression in Parkinsonian patients: A randomized controlled trial with 1‐year follow‐up. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2012;26(2):144‐50. - PubMed
Gobbi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gobbi L, Oliveira‐Ferreira M, Aetano MJ, irani‐Silva E, Arbieri F, Tella F, et al. Exercise programs improve mobility and balance in people with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2009; Vol. 15 Suppl 2:S6. - PubMed
-
- Gobbi LTB, Oliveira‐Ferreira MDT, Caetano MJD, Lirani‐Silva E, Barbieri FA, Stella F, et al. Exercise programs improve mobility and balance in people with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2009;15 Suppl 3:S49‐52. - PubMed
Haase 2011 {published data only}
-
- Haase M. The immediate effects of rhythmic arm swing and finger tapping exercises on gait of Parkinson's patients. ProQuest 2011.
Kamsma 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kamsma YPT, Brouwer WH, Lakke JPWF. Training of compensational strategies for impaired gross motor skills in Parkinson' disease. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice 1995;11(4):209‐29.
Klassen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Klassen L, Dal Bello‐Haas V, Sheppard M, Metcalfe A. Evaluating the benefits of group exercise and group exercise and education programs for individuals with Parksinson's disease (PD). Physiotherapy 2007;93 Suppl 1:S91.
Knobl 2011 {published data only}
-
- Knobl PE. An evaluation of motor imagery and exercise interventions in Parkinson's disease. ProQuest 2011.
-
- Knobl PE, Almeida QJ. Rehabilitation for Parkinson's disease: Is it the sensory or attention focus that improves disease severity in sensory‐attention focused interventions?. Movement Disorders 2011;26 Suppl 2:s153.
Lee 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lee KS, Lee WH, Hwang S. Modified constraint‐induced movement therapy improves fine and gross motor performance of the upper limb in Parkinson disease. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2011;90(5):380‐6. - PubMed
Ma 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ma HI, Hwang WJ, Lin KC. The effects of two different auditory stimuli on functional arm movement in persons with Parkinson's disease: a dual‐task paradigm. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009;23(3):229‐37. - PubMed
Marchese 2000 {published data only}
-
- Abbruzzese G, Diverio M, Zucchi F, Marchese R. Comparison of two physical therapy approaches in the rehabilitation of parkinsonian patients. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 1999;5 Suppl:S49. - PubMed
-
- Marchese R, Diverio M, Zucchi F, Lentino C, Abbruzzese G. Comparison of two physical therapy approaches in the rehabilitation of parkinsonian patients: a comparison of two physical therapy protocols. Movement Disorders 2000;15(5):879‐83. - PubMed
Modugno 2010 {published data only}
-
- Modugno N. Long‐term program of social theatre for the management of motor and motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010; Vol. 25 Suppl 3:S721.
Munneke 2010 {published data only}
-
- Keus SH, Bloem BR, Nijkrake M, Lim LI, Munneke M. The ParkNet trial: Implementation of an evidence‐based guideline for physical therapy in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2006;21:S122.
-
- Keus SHJ, Nijkrake MJ, Borm GF, Kwakkel G, Roos RAC, Berendse HW, et al. The ParkinsonNet trial: design and baseline characteristics. Movement Disorders 2010;25(7):830‐7. - PubMed
-
- Munneke M, Kens S, Nijkrake M, Kwakkel G, Berendse H, Roos R, et al. Efficiency of evidence‐based physiotherapy for Parkinson's disease: the ParkinsonNet Trial. Movement Disorders 2008;23 Suppl 1:669.
-
- Munneke M, Nijkrake M, Keus SHJ, Kwakkel G, Berendse HW, Roos RAC, et al. Efficacy of community‐based physiotherapy networks for patients with Parkinson's disease: a cluster‐randomised trial. Lancet Neurology 2010;9(1):46‐54. - PubMed
-
- Munneke M, Nijkrake MJ, Keus SHJ, Lim IIK, Borm GF, Wilt GJ, et al. Efficiency of physiotherapy in Parkinson's disease: The ParkNet trial. Movement Disorders 2007;22 Suppl 16:629.
Pacchetti 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pacchetti C, Mancini F, Aglieri R, Fundaro C, Martignoni E, Nappi G. Active music therapy in Parkinson's disease: An integrative method for motor and emotional rehabilitation. Psychosomatic Medicine 2000;62(3):386‐93. - PubMed
Pohl 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pohl M, Rockstroh G, Ruckriem S, Mrass G, Mehrholz J. Immediate effects of speed‐dependent treadmill training on gait parameters in early Parkinson's disease. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2003;84(12):1760‐6. - PubMed
Rochester 2011 {published data only}
-
- Rochester L, Baker K, Nieuwboer A, Burn D. Targeting dopa‐sensitive and dopa‐resistant gait dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: selective responses to internal and external cues. Movement Disorders 2011;26(3):430‐5. - PubMed
Sage 2009a {published data only}
-
- Sage MD, Almeida QJ. Symptom and gait changes after sensory attention focused exercise vs aerobic training in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24(8):1132‐8. - PubMed
Sage 2009b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sage MD, Almeida QJ. A Canadian approach to exercise rehabilitation: a systematic evaluation of strategies to reduce the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24 Suppl 1:S276‐7.
Sage 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sage MD, Almeida QJ. A positive influence of vision on motor symptoms during sensory attention focused exercise for Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25(1):64‐9. - PubMed
Stallibrass 2001 {published data only}
-
- Stallibrass C. Controlled trial to evaluate the effects of lessons in the Alexander Technique on the management of disability by people with Parkinson's disease. National Research Register 2001.
Tamir 2007 {published data only}
-
- Tamir R, Dickstein R, Huberman M. Integration of motor imagery and physical practice in group treatment applied to subjects with Parkinson's disease. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2007;21(1):68‐75. - PubMed
Tickle‐Degnen 2010 {published data only}
-
- White DK, Wagenaar RC, Ellis TD, Tickle‐Degnen L. Changes in walking activity and endurance following rehabilitation for people with Parkinson disease. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90(1):43‐50. - PubMed
Wulf 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wulf G, Landers M, Lewthwaite R, Tollner T. External focus instructions reduce postural instability in individuals with Parkinson's disease. Physical Therapy 2009;89(2):162‐8. - PubMed
Yen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yen CY, Lin KH, Hu MH, Wu RM, Lu TW, Lin CH, et al. Effects of virtual reality‐augmented balance training on sensory organization and attentional demand for postural control in people with Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. Physical Therapy 2011;91(6):862‐78. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Brauer 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Protas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Protas EJ, Mitchell K, Williams A, Qureshy H, Caroline K, Lai EC. Gait and step training to reduce falls in Parkinson's disease. NeuroRehabilitation 2005;20(3):183‐90. - PubMed
Schenkman 2012b {published data only}
-
- Schenkman M. Endurance exercise in Parkinson's disease. controlled_trials.com 2012.
-
- Schenkman M. Study in Parkinson's disease of exercise (SPARX). ClinicalTrials.gov 2011.
Smith 2009 {published data only}
-
- Smith S, Dibble L. High force resistance training and dopamine replacement effects on hypokinesia in Parkinson disease. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009.
Uc 2010 {published data only}
-
- Uc EY, Newman SR. Effects of aerobic exercise in Parkinson's disease. ClinicalTrials.gov 2010.
van Nimwegen 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Speelman AD, Nimwegan M, Smulders K, Overeem S, Borm G, Backx F, et al. Rationale and design of the Parkfit study: a randomized controlled trial to increase physical activity in patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2010; Vol. 16 Suppl 1:S58.
-
- Nimwegen M, Speelman A, Smulders S, Overeem S, Borm G, Backx F, et al. Rationale and design of the ParkFit study: A randomized controlled trial to increase physical activity in patient with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24 Suppl 1:S284.
-
- Nimwegen M, Speelman AD, Smulders K, Overeem S, Borm GF, Backx FJG, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the ParkFit study, a randomized controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of a multifaceted behavioral program to increase physical activity in Parkinson patients. BMC Neurology 2010;10:70. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nimwegen ML, Speelman AD, Gerrits MS, Bloem BR, Munneke M. Monitoring treatment fidelity in the ParkFit Study, a multifaceted behavioral program to increase physical activity in Parkinson patients. Movement Disorders 2010; Vol. 25 Suppl 3:S678.
Additional references
Allen 2011
-
- Allen NE, Sherrington C, Paul SS, Canning CG. Balance and falls in Parkinson's disease: a meta‐analysis of the effect of exercise and motor training. Movement Disorders 2011;26(9):1605‐15. - PubMed
Berg 1992
-
- Berg KO, Wooddauphinee SL, Williams JI. Measuring balance in the elderly ‐ validation of an instrument. Canadian Journal of Public Health‐Revue Canadienne de Sante Publique 1992;83:S7‐S11. - PubMed
Boutron 2008a
-
- Boutron I, Moher D, Altman DG, Schulz K, Ravaud P, for the CONSORT group. Methods and processes of the CONSORT Group: example of an extension for trials assessing nonpharmacologic treatments. Annals of Internal Medicine 2008;148(4):W60‐6. - PubMed
Boutron 2008b
-
- Boutron I, Moher D, Altman DG, Schulz K, Ravaud P, for the CONSORT group. Extending the CONSORT statement to randomized trials of nonpharmacologic treatment: explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine 2008;148(4):295‐309. - PubMed
Chartered Society of Physiotherapy
-
- The Chartered Society of Physiotherapy. In: The Chartered Society of Physiotherapy, editor(s). Rules of professional conduct. 2nd Edition. London: The Chartered Society of Physiotherapy, 2002.
Crizzle 2006
-
- Crizzle AM, Newhouse IJ. Is physical exercise beneficial for persons with Parkinson's disease?. Clinical Journal of Sports Medicine 2006;16(5):422‐5. - PubMed
Deane 2001a
-
- Deane K, Jones DE, Playford ED, Ben‐Shlomo Y, Clarke CE. Physiotherapy versus placebo or no intervention in Parkinson's disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, (3):CD002817.
Deboer 1996
Doll 1980
Duncan 1990
-
- Duncan PW, Weiner DK, Chandler J, Studenski S. Functional Reach ‐ A new clinical measure of balance. Journals of Gerontology 1990;45(6):M192‐7. - PubMed
Fahn 1987
-
- Fahn S, Elton RL. UPDRS Development Committee. Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB, Goldestein M editor(s). Recent developments in Parkinson's disease. Florham Park, NJ: Macmillan Health Care Information, 1987:153‐63.
Gage 2004
-
- Gage H, Storey L. Rehabilitation for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review of available evidence. Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;18(5):463‐82. - PubMed
Gibb 1988
Giladi 2000
-
- Giladi N, Shabtai H, Simon ES, Biran S, Tal J, Korczyn AD. Construction of freezing of gait questionnaire for patients with Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2000;6(3):165‐70. - PubMed
Goodwin 2008
-
- Goodwin VA, Richards SH, Taylor RS, Taylor AH, Campbell JL. The effectiveness of exercise interventions for people with Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Movement Disorders 2008;23(5):631‐40. - PubMed
Hoehn 1967
-
- Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism ‐ onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 1967;17(5):427‐42. - PubMed
Jenkinson 1997
-
- Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R, Peto V, Greenhall R, Hyman N. The Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ‐39): development and validation of a Parkinson's disease summary index score. Age and Ageing 1997;26(5):353‐7. - PubMed
Kersten 2004
-
- Kersten P. Principles of physiotherapy assessment and outcome measures. In: Stokes M editor(s). Physical management in neurological rehabilitation. 2nd Edition. London: Elsevier Mosby, 2004:29‐46.
Keus 2004
-
- Keus S, Hendriks HJ, Bloem BR, Bredero‐Cohen AB, Goede CJ, Haaren M, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for physical therapy in patients with Parkinsons disease. Dutch Journal of Physiotherapy 2004;114 Suppl 3:1‐94.
Keus 2007
-
- Keus SHJ, Bloem BR, Hendriks EJM, Bredero‐Cohen AB, Munneke M. Evidence‐based analysis of physical therapy in Parkinson's disease with recommendations for practice and research. Movement Disorders 2007;22(4):451‐60. - PubMed
Keus 2009
-
- Keus SHJ, Munneke M, Nijkrake MJ, Kwakkel G, Bloem BR. Physical therapy in Parkinson's disease: Evolution and future challenges. Movement Disorders 2009;24(1):1‐14. - PubMed
Kwakkel 2007
-
- Kwakkel G, Goede CJT, Wegen EEH. Impact of physical therapy for Parkinson's disease: A critical review of the literature. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2007;13:S478‐87. - PubMed
Lim 2005
-
- Lim I, Wegen E, Goede C, Deutekom M, Nieuwboer A, Willems A, et al. Effects of external rhythmical cueing on gait in patients with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Clinical Rehabilitation 2005;19(7):695‐713. - PubMed
Mehrholz 2010
-
- Mehrholz J, Friis R, Kugler J, Twork S, Storch A, Pohl M. Treadmill training for patients with Parkinson's disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, (1):CD007830. - PubMed
MRC 2008
-
- Medical Research Council. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: new guidance. http://www.mrc.ac.uk/Utilities/Documentrecord/index.htm?d=MRC004871 2008.
Mutch 1986
NICE CG35 2006
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. NICE clinical guideline 35. Parkinson's disease: diagnosis and management in primary and secondary care. www.nice.org.uk 2006.
Nieuwboer 2008
-
- Nieuwboer A, Rochester L, Jones D. Cueing gait and gait‐related mobility in patients with Parkinson's disease ‐ Developing a therapeutic method based on the international classification of functioning, disability, and health. Topics in Geriatric Rehabilitation 2008;24(2):151‐65.
Nijkrake 2007
-
- Nijkrake MJ, Keus SH, Kalf JG, Sturkenboom IH, Munneke M, Kappelle AC, Bloem BR. Allied health care interventions and complementary therapies in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2007;13 Suppl 3:S488‐94. - PubMed
Patel 2010
-
- Patel S, Cheed V, Ives N, Clarke C, Rick C, Wheatley K, Gray R, on behalf of the PD MED Collaborators. A large randomised assessment of the relative cost‐effectiveness of different classes of drugs for Parkinson's disease (PD MED Trial). Movement Disorders 2010;25 Suppl 3:S681.
PDS 2008
-
- PDS. Life with Parkinson's today ‐ room for improvement. Parkinson's Disease Society, London 2008.
Perry 1995
-
- Perry J, Garrett M, Gronley JK, Mulroy SJ. Classification of walking handicap in the stroke population. Stroke 1995;26(6):982‐9. - PubMed
Peto 1995
-
- Peto V, Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R, Greenhall R. The development and validation of a short measure of functioning and well‐being for individuals with Parkinson's disease. Quality of Life Research 1995;4(3):241‐8. - PubMed
Peto 2001
-
- Peto V, Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R. Determining minimally important differences for the PDQ‐39 Parkinson's disease questionnaire. Age and Ageing 2001;30:299‐302. - PubMed
Plant 2000
-
- Plant R, Jones D, Walton G, Ashburn A, Lovgreen B, Handford F, Kinnear E. Physiotherapy for people with Parkinson's disease: UK best practice short report. Institution of Rehabilitation, University of Northumbria 2000.
Podsiadlo 1991
-
- Podsiadlo D, Richardson S. The Timed Up and Go ‐ A test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1991;39(2):142‐8. - PubMed
Powell 1995
-
- Powell LE, Myers AM. The Activities‐Specific Balance Confidence (Abc) Scale. Journals of Gerontology Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 1995;50(1):M28‐34. - PubMed
Qutubuddin 2005
-
- Qutubuddin AA, Pegg PO, Cifu DX, Brown R, McNamee S, Carne W. Validating the Berg Balance Scale for patients with Parkinson's disease: A key to rehabilitation evaluation. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2005;86(4):789‐92. - PubMed
Rascol 2002
-
- Rascol O, Payoux P, Ferreira J, Brefel‐Courbon C. The management of patients with early Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2002;9(1):61‐7. - PubMed
Robertson 2003
-
- Robertson D. Developing and delivering services. In: Playford D, Thompson AJ editor(s). Neurological Rehabilitation of Parkinson's Disease. London: Martin Dunitz, 2003.
Robertson 2008
-
- Robertson D, Aragon A, Moore G, Whelan L. Rehabilitation and the interdisciplinary team. In: Playfer J, Hindle J editor(s). Parkinson's Disease in the Older Patient. 2nd Edition. Oxford: Radcliffe Publishing Ltd, 2008.
Rubenis 2007
-
- Rubenis J. A rehabilitational approach to the management of Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2007;13 Suppl 3:S495‐7. - PubMed
Schrag 2000
-
- Schrag A, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N. How does Parkinson's disease affect quality of life? A comparison with quality of life in the general population. Movement Disorders 2000;15(6):1112‐8. - PubMed
Schrag 2006
-
- Schrag A, Sampaio C, Counsell N, Poewe W. Minimal clinically important change on the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale. Movement Disorders 2006;21(8):1200‐7. - PubMed
Shulman 2010
-
- Shulman LM, Gruber‐Baldini AL, Anderson KE, Fishman PS, Reich SG, Weiner WJ. The clinically important difference on the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale. Archives of Neurology 2010;67(1):64‐70. - PubMed
Steffen 2008
-
- Steffen T, Seney M. Test‐retest reliability and minimal detectable change on balance and ambulation tests, the 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey, and the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale in people with parkinsonism. Physical Therapy 2008;88(6):733‐46. - PubMed
Talley 2008
-
- Talley KMC, Wyman JF, Gross CR. Psychometric properties of the activities‐specific balance confidence scale and the survey of activities and fear of falling in older women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2008;56(2):328‐33. - PubMed
Tinetti 1990
-
- Tinetti ME, Richman D, Powell L. Falls efficacy as a measure of fear of falling. Journals of Gerontology 1990;45(6):239‐43. - PubMed
Tomlinson 2012
-
- Tomlinson CL, Patel S, Meek C, Clarke CE, Stowe R, Shah L, et al. Physiotherapy versus placebo or no intervention in Parkinson's disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, (8):CD002817. - PubMed
Trew 2005
-
- Trew M, Everett T. Human movement: an introductory text. 5th Edition. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2005.
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey (Sf‐36) .1. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473‐83. - PubMed
Webster 1968
-
- Webster DD. Critical analysis of disability in Parkinson's disease. Modern Treatment 1968;5(2):257‐82. - PubMed
Welsh 2003
-
- Welsh M, McDermott MP, Holloway RG, Plumb S, Pfeiffer R, Hubble J, et al. Development and testing of the Parkinson's disease quality of life scale. Movement Disorders 2003;18(6):637‐45. - PubMed
Whittle 1996
-
- Whittle M. Gait analysis: an introduction. 2nd Edition. Oxford: Butterworth‐Heinemann, 1996.
Yahr 1969
-
- Yahr MD, Duvoisin RC, Schear MJ, Barrett RE, Hoehn MM. Treatment of Parkinsonism with levodopa. Archives of Neurology 1969;21(4):343‐54. - PubMed
Yardley 2005
-
- Yardley L, Beyer N, Hauer K, Kempen G, Piot‐Ziegler C, Todd C. Development and initial validation of the Falls Efficacy Scale‐International (FES‐I). Age and Ageing 2005;34(6):614‐9. - PubMed
Yarrow 1999
-
- Yarrow S. Members' 1998 survey of the Parkinson's Disease Society of the United Kingdom. In: Percival R, Hobson P editor(s). Parkinson's disease: Studies in psychological and social care. Leicester: BPS Books, 1999:79‐92.
References to other published versions of this review
Deane 2001b
-
- Deane K, Jones DE, Ellis‐Hill C, Clarke CE, Playford ED, Ben‐Shlomo Y. Physiotherapy for Parkinson's disease: a comparison of techniques. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, (1):CD002815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous