Imaging of acute stroke prior to treatment: current practice and evolving techniques
- PMID: 24936980
- PMCID: PMC4112390
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20140216
Imaging of acute stroke prior to treatment: current practice and evolving techniques
Abstract
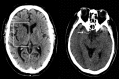
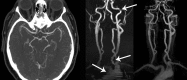
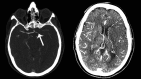
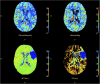
Standard imaging in acute stroke is undertaken with the aim of diagnosing the underlying cause and excluding stroke mimics. In the presence of ischaemic stroke, imaging is also needed to assess patient suitability for treatment with intravenous thrombolysis. Non-contrast CT is predominantly used, but MRI can also exclude any contraindications to thrombolysis treatment. Advanced stroke imaging such as CT and MR angiography and perfusion imaging are increasingly used in an acute setting. In this review, we discuss the evidence for the application of these advanced techniques in the imaging of acute stroke.
Figures

References
-
- Mathers CD, Bernand C, Iburg KM, Inoue M, Ma Fat D, Shibuya K, et al. . Global burden of disease: data sources, methods and results. World Health Organization; 2004. [Cited 30 June 2014.] Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/en/
-
- The International Stroke Trial (IST): a randomised trial of aspirin, subcutaneous heparin, both, or neither among 19435 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. International Stroke Trial Collaborative Group. Lancet 1997; 349: 1569–81. - PubMed
-
- Dombrowski SU, Mackintosh JE, Sniehotta FF, Araujo-Soares V, Rodgers H, Thomson RG, et al. . The impact of the UK “Act FAST” stroke awareness campaign: content analysis of patients, witness and primary care clinicians' perceptions. BMC Public Health 2013; 13: 915. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-915 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

