Bronchodilators for bronchiolitis
- PMID: 24937099
- PMCID: PMC7055016
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001266.pub4
Bronchodilators for bronchiolitis
Abstract
Background: Bronchiolitis is an acute, viral lower respiratory tract infection affecting infants and is sometimes treated with bronchodilators.
Objectives: To assess the effects of bronchodilators on clinical outcomes in infants (0 to 12 months) with acute bronchiolitis.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL 2013, Issue 12, MEDLINE (1966 to January Week 2, 2014) and EMBASE (1998 to January 2014).
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing bronchodilators (other than epinephrine) with placebo for bronchiolitis.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors assessed trial quality and extracted data. We obtained unpublished data from trial authors.
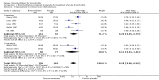
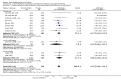
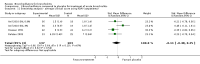
Main results: We included 30 trials (35 data sets) representing 1992 infants with bronchiolitis. In 11 inpatient and 10 outpatient studies, oxygen saturation did not improve with bronchodilators (mean difference (MD) -0.43, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.92 to 0.06, n = 1242). Outpatient bronchodilator treatment did not reduce the rate of hospitalization (11.9% in bronchodilator group versus 15.9% in placebo group, odds ratio (OR) 0.75, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.21, n = 710). Inpatient bronchodilator treatment did not reduce the duration of hospitalization (MD 0.06, 95% CI -0.27 to 0.39, n = 349).Effect estimates for inpatients (MD -0.62, 95% CI -1.40 to 0.16) were slightly larger than for outpatients (MD -0.25, 95% CI -0.61 to 0.11) for oximetry. Oximetry outcomes showed significant heterogeneity (I(2) statistic = 81%). Including only studies with low risk of bias had little impact on the overall effect size of oximetry (MD -0.38, 95% CI -0.75 to 0.00) but results were close to statistical significance.In eight inpatient studies, there was no change in average clinical score (standardized MD (SMD) -0.14, 95% CI -0.41 to 0.12) with bronchodilators. In nine outpatient studies, the average clinical score decreased slightly with bronchodilators (SMD -0.42, 95% CI -0.79 to -0.06), a statistically significant finding of questionable clinical importance. The clinical score outcome showed significant heterogeneity (I(2) statistic = 73%). Including only studies with low risk of bias reduced the heterogeneity but had little impact on the overall effect size of average clinical score (SMD -0.22, 95% CI -0.41 to -0.03).Sub-analyses limited to nebulized albuterol or salbutamol among outpatients (nine studies) showed no effect on oxygen saturation (MD -0.19, 95% CI -0.59 to 0.21, n = 572), average clinical score (SMD -0.36, 95% CI -0.83 to 0.11, n = 532) or hospital admission after treatment (OR 0.77, 95% CI 0.44 to 1.33, n = 404).Adverse effects included tachycardia, oxygen desaturation and tremors.
Authors' conclusions: Bronchodilators such as albuterol or salbutamol do not improve oxygen saturation, do not reduce hospital admission after outpatient treatment, do not shorten the duration of hospitalization and do not reduce the time to resolution of illness at home. Given the adverse side effects and the expense associated with these treatments, bronchodilators are not effective in the routine management of bronchiolitis. This meta-analysis continues to be limited by the small sample sizes and the lack of standardized study design and validated outcomes across the studies. Future trials with large sample sizes, standardized methodology across clinical sites and consistent assessment methods are needed to answer completely the question of efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ann Gadomski is a trialist in included studies and is a member of the AAP Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Management of Bronchiolitis. Melissa Scribani: none known.
Figures
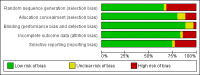









Update of
-
Bronchodilators for bronchiolitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Dec 8;(12):CD001266. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001266.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 17;(6):CD001266. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001266.pub4. PMID: 21154348 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Alario 1992 {published data only}
-
- Alario AJ, Lewander WJ, Dennehy P, Seifer R, Mansell AL. The efficacy of nebulized metaproterenol in wheezing infants and young children. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1992;146:412‐8. - PubMed
Anil 2010 SAL 0.9% {published data only}
-
- See Anil 2010 SAL 3.0%.
Anil 2010 SAL 3% {published data only}
-
- Anil AB, Anil M, Saglam AB, Cetin N, Bal A, Aksu N. High volume normal saline alone is as effective as nebulized salbutamol‐normal saline, epinephrine‐normal saline, and 3% saline in mild bronchiolitis. Pediatric Pulmonology 2010;45:41‐7. - PubMed
Can 1998 {published data only}
-
- Can D, Inan G, Yendur G, Oral R, Günay I. Salbutamol or mist in acute bronchiolitis. Acta Paediatrica Japonica 1998;40(3):252‐5. - PubMed
Chevallier 1995 {published data only}
-
- Chevallier B, Aegerter P, Parat S, Bidat E, Renaud C, Lagardere B. Comparative study of nebulized sambutol against placebo in the acute phase of bronchiolitis in 33 infants aged 1 to 6 months [Etude comparative des nebulisations de salbutamol contre placebo a la phase aigue d'une bronchiolite chez 33 nourrissons de 1 a 6 mois]. Archives de Pédiatrie 1995;2(1):11‐7. - PubMed
Chowdhury 1995 {published data only}
-
- Chowdhury D, Al Howasi M, Khalil M, Al‐Frayh AS, Chowdhury S, Ramia S. The role of bronchodilators in the management of bronchiolitis: a clinical trial. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 1995;15:77‐84. - PubMed
Dobson 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dobson JV, Stephen‐Groff SM, McMahon SR, Stemmler MM, Brallier SL, Bay C. The use of albuterol in hospitalized infants with bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 1998;101:361‐8. - PubMed
Gadomski 1994a ‐ neb {published data only}
-
- Gadomski AM, Aref GH, Din OB, Sawy IH, Khallaf N, Black RE. Oral versus nebulized albuterol in the management of bronchiolitis in Egypt. Journal of Pediatrics 1994;124:131‐8. - PubMed
Gadomski 1994a ‐ oral {published data only}
-
- See Gadomski 1994a ‐ neb.
Gadomski 1994b ‐ neb {published data only}
-
- Gadomski AM, Lichenstein R, Horton L, King J, Keane V, Permutt T. Efficacy of albuterol in the management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 1994;93:907‐12. - PubMed
Gadomski 1994b ‐ oral {published data only}
-
- See Gadomski 1994b ‐ neb.
Goh 1997 {published data only}
-
- Goh A, Chay OM, Foo AL, Ong EK. Efficacy of bronchodilators in the treatment of bronchiolitis. Singapore Medical Journal 1997;38:326‐8. - PubMed
Gupta 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gupta P, Aggarwal A, Gupta P, Sharma KK. Oral salbutamol for symptomatic relief in mild bronchiolitis: a double blind randomized placebo controlled trial. Indian Pediatrics 2008;45:547‐53. - PubMed
Gurkan 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gurkan F, Tuzun H, Ece A, Haspolat K, Bosnak M, Dikici B. Comparison of treatments with nebulized salbutamol and epinephrine in acute bronchiolitis [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2004;24(Suppl 48):344.
Henry 1983 {published data only}
Ho 1991 {published data only}
Ipek 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ipek IO, Yalcin EU, Sezer RG, Bozaykut A. The efficacy of nebulized salbutamol, hypertonic saline and salbutamol/hypertonic saline combination in moderate bronchiolitis. Pulmonary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2011;24:633‐7. - PubMed
Karadag 2005 ‐ IPR {published and unpublished data}
-
- Karadag B, Ceran O, Dursun E, Guven G, Ozahi I, Karakoc F, et al. Efficacy of bronchodilators in acute bronchiolitis [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 2000;16(Suppl 31):562. [CN‐00415977]
-
- Karadag B, Ceran O, Guven G, Dursun E, Ozahi I, Karakoc F, et al. The role of bronchodilators in the management of acute bronchiolitis. Unpublished manuscript 2005.
-
- Karadag B, Cerna O, Dursun E, Guven G, Ozahi I, Karakoc F, et al. Comparison of bronchodilators in acute bronchiolitis [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. 2002. [CN‐00429340]
Karadag 2005 ‐ SAL {published and unpublished data}
-
- See Karadag 2005 ‐ IPR.
Karadag 2008 {published data only}
-
- Karadag B, Ceran O, Guven G, Dursun E, Ipek IO, Karakoc F, et al. Efficacy of salbutamol and ipratropium bromide in the management of acute bronchiolitis ‐ a clinical trial. Respiration 2008;76:283‐7. - PubMed
Klassen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Klassen TP, Rowe PC, Sutcliffe T, Ropp LJ, McDowell IW, Li MM. Randomized trial of salbutamol in acute bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 1991;118:807‐11. - PubMed
Levin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Levin DL, Garg A, Hall LJ, Slogic S, Jarvis JD, Leiter JC. A prospective randomized controlled blinded study of three bronchodilators in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis on mechanical ventilation. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2008;9:598‐604. - PubMed
Lines 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lines DR, Kattampallil JS, Liston P. Efficacy of nebulized salbutamol in bronchiolitis. Pediatric Reviews & Communications 1990;5:121‐9.
Lines 1992 {published data only}
-
- Lines DR, Bates ML, Rechtman AR. Efficacy of nebulized ipratropium bromide in acute bronchiolitis. Pediatric Reviews & Communications 1992;6:161‐7.
Mallol 1987 {published data only}
-
- Mallol J, Barrueto L, Girardi G, Munoz R, Puppo H, Ulloa V, et al. Use of nebulized bronchodilators in infants under 1 year of age: analysis of four forms of therapy. Pediatric Pulmonology 1987;3:298‐303. - PubMed
Patel 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Patel H, Platt RW, Pekeles GS, Ducharme FM. A randomized, controlled trial of the effectiveness of nebulized therapy with epinephrine compared with albuterol and saline in infants hospitalized for acute viral bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141(6):818‐24. - PubMed
Patel 2003 {published data only}
-
- Patel H, Gouin S, Platt RW. Randomized, double‐bind, placebo‐controlled trial of oral albuterol in infants with mild‐to‐moderate acute viral bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 2003;142:509‐14. - PubMed
Ralston 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ralston S, Hartenberger C, Anaya T, Qualls C, Kelly HW. Randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of albuterol and epinephrine at equipotent beta‐2 agonist doses in acute bronchiolitis. Pediatric Pulmonology 2005;40:292‐9. - PubMed
Scarlett 2012 {published data only}
-
- Scarlett EE, Walker S, Rovitelli A, Ren CL. Tidal breathing responses to albuterol and normal saline in infants with viral bronchiolitis. Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology 2012;25:220‐5.
Schuh 1990 {published data only}
-
- Schuh S, Canny G, Reisman JJ, Kerem E, Bentur L, Petric M, et al. Nebulized albuterol in acute bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 1990;117:633‐7. - PubMed
Schweich 1992 {published data only}
-
- Schweich PJ, Hurt TL, Walkley EI, Mullen N, Archibald LF. The use of nebulized albuterol in wheezing infants. Pediatric Emergency Care 1992;8:184‐8. - PubMed
Tal 1983 {published data only}
-
- Tal A, Bavilski C, Yohai D, Bearman JE, Gorodischer R, Moses SW. Dexamethasone and salbutamol in the treatment of acute wheezing in infants. Pediatrics 1983;71:13‐8. - PubMed
Tinsa 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tinsa F, Rhouma AB, Ghaffari H, Zouari B, Brini I, Karboul L, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of nebulized terbutaline for the first acute bronchiolitis in infants less than 12‐months‐old. Tunisie Medicale 2009;87:200‐3. - PubMed
Totapally 2002 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Absar 2008 {published data only}
-
- Absar SMN, Jahan S, Khanum S. Efficacy of nebulized ipratropium bromide versus salbutamol in infants with acute bronchiolitis. Bangladesh Medical Research Council Bulletin 2008;34(3):112. - PubMed
Abu‐Shukair 2001 {published data only}
-
- Abu‐Shukair M, El‐Tal Y, Al‐Rawabdeh E. Salbutamol versus epinephrine in the treatment of acute bronchiolitis. Journal of the Bahrain Medical Society 2001;13(3):143‐6.
Alansari 2013 {published data only}
-
- Alansari K, Sakran M, Davidson BL, Ibrahim K, Alrefai M, Zakaria I. Oral dexamethasone for bronchiolitis: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 2013;132(1):e810‐6. - PubMed
Barlas 1998 {published data only}
-
- Barlas C, Kiper N, Gocmen A, Ozcelik U, Dilber E, Anadol D, et al. Racemic adrenaline and other treatment regimens in mild and moderate bronchiolitis [Hafif ve orta siddetteki bronsiolit vakalarinda rasemik adrenalin ve diger tedavi yontemlerinin karsilastirilmasi]. Cocuk Sagligi Ve Hastaliklari Dergisi 1998;41:155–65.
Beck 2007 {published data only}
Belcastro 2010 {published data only}
-
- Belcastro MR, Backes CR, Chila AG. Bronchiolitis: a pilot study of osteopathic manipulative treatment, bronchodilators, and other therapy. Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 2010;83(9):672‐6. - PubMed
Bentur 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bentur L, Beck R, Shoval S, Elias N, Naveh T, Godfrey S. Nebulized epinephrine versus albuterol for treatment of RSV bronchiolitis. American Thoracic Society 99th International Conference. 2003:C093 Poster 703.
Bertrand 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bertrand P, Aranibar H, Castro E, Sanchez I. Efficacy of nebulized epinephrine versus salbutamol in hospitalized infants with bronchiolitis. Pediatric Pulmonology 2001;31:284‐8. - PubMed
Brooks 1981 {published data only}
-
- Brooks LJ, Cropp GJA. Theophylline therapy in bronchiolitis. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1981;135:934‐6. - PubMed
Cengizlier 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cengizlier R, Saraclar Y, Adalioglu G, Tuncer A. Effect of oral and inhaled salbutamol in infants with bronchiolitis. Acta Paediatrica Japonica 1997;39:61‐3. - PubMed
Chao 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chao LC, Lin YZ, Wu WF, Huang FY. Efficacy of nebulized budesonide in hospitalized infants and children younger than 24 months with bronchiolitis. Acta Paediatrica Taiwanica 2003;44(6):332‐5. - PubMed
Choong 1998 {published data only}
-
- Choong CS, Huang YF, Liew KL, Liu PN, Tsai DH, Cheng IY, et al. The efficacy of nebulized beta‐2 agonist bronchodilator therapy in the treatment of acute bronchiolitis. Tsu Chi Medical Journal 1998;10(2):95‐101.
Cortes 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cortes ME, Graniel GJ. Administration of nebulized salbutamol versus placebo in infants with bronchiolitis. Practica Pediatrica 1996;5(7):18‐9.
Del Vecchio 2012 {published data only}
Fernandez 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez CI, Fernandez BH, Navarro CM, Soler MG, Lopez PV, Pardillo RM. Heliox‐driven bronchodilator nebulization in the treatment of infants with bronchiolitis. Annals of Pediatrics 2009;70:40‐4. - PubMed
Ferrer 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ferrer C, Gaig P, Marin A, et al. Bromuro de ipratropio en las bronquiolitis. Revista Espanola de Alergologia e Immunologia Clinica 1990;5(Suppl 1):83‐4.
Florin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Florin TA, Kittick M, Shaw KN, Zorc JJ. A randomized trial of nebulized hypertonic saline for bronchiolitis in the emergency department. Pediatric Emergency Care 2012;28(9):1096. - PubMed
Frasson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Frasson T, Nascimento‐Junior G, Frasson F, Rossi M, Rodrigues A, Goncalves W, et al. Increase in induced expiratory flow reduces peripheral hypoxemia in children with acute bronchiolitis. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2012;13(5):618.
Goebel 2000 {published data only}
-
- Goebel J, Estrada B, Quinonez J, Nagji N, Sanford D, Boerth RC. Prednisolone plus albuterol versus albuterol alone in mild to moderate bronchiolitis. Clinical Pediatrics 2000;39(4):213‐20. - PubMed
Gomez‐y‐Lopez 2007 {published data only}
-
- Gomez‐y‐Lopez RE, Hernandez‐Sierra JF, Torres‐Ruvalcaba BA, Martinez‐Puente E, Carmen Martinez‐Garcia M. Comparative clinical study of dexamethasone vs. nebulized salbutamol in acute bronchiolitis. Gaceta Medica de Mexico 2007;142(3):189‐92. - PubMed
Gonzalez 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez PYE, Ruiz BA, Garate AJ, Romero IC, Bone CJ, Arranz AL, et al. A multicenter randomized, open, parallel group study comparing different treatments for hospitalized infants with acute wheezy bronchitis. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1994;14(5):315‐9.
Hammer 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hammer J, Numa A, Newth CJL. Albuterol responsiveness in infants with respiratory failure caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatric Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1995;127(3):485‐90. - PubMed
John 2006 {published data only}
John 2010 {published data only}
Kadir 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kadir MA, Mollah AH, Basak R, Choundhury AM, Ahmed S. Comparative efficacy of combined nebulized salbutamol with ipratropium bromide and nebulized adrenaline to treat children with acute bronchiolitis. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2009;18(2):208‐14. - PubMed
Karaatmaca 2010 {published data only}
-
- Karaatmaca B, Aydogan M, Piraneci R, Bicer S. Comparison of the effectiveness of nebulized budesonide, salbutamol and adrenaline in the treatment of acute bronchiolitis: a randomized double blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Allergy 2010;65(Suppl 92):716.
Kim 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kim IK, Phrampus E, Sikes K, Pendleton J, Saville A, Corcoran T, et al. Helium‐oxygen therapy for infants with bronchiolitis: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2011;165(12):1115‐22. - PubMed
Langley 2005 {published data only}
Luo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Luo AW, Ma HH, Zhou W, Xie XA. The clinical observation of budesonide and terbutaline aerosol on the treatment of bronchiolitis. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy 2003;23(9):549‐50.
Luo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Luo A, Lui E, Luo J, Li S, Zeng F, Yang X, et al. Nebulized hypertonic saline/salbutamol solution treatment in hospitalized children with mild to moderate bronchiolitis. Pediatrics International 2010;52:199‐202. - PubMed
Luo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Luo Z, Liu E, Luo J, Li S, Zeng F, Yang X, et al. Nebulized hypertonic saline/salbutamol solution treatment in hospitalized children with mild to moderate bronchiolitis. Pediatrics International 2010;52(2):199‐202. - PubMed
Mandelberg 2003 {published data only}
-
- Mandelberg A, Tal G, Witzling M, Someck E, Houri S, Balin A, et al. Nebulized 3% hypertonic saline solution treatment in hospitalized infants with viral bronchiolitis. Chest 2003;123:481‐7. - PubMed
Menon 1995 {published data only}
-
- Menon K, Sutcliffe T, Klassen TP. A randomized trial comparing the efficacy of epinephrine with salbutamol in the treatment of acute bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 1995;126(6):1004‐7. - PubMed
Milner 1995 {published data only}
-
- Milner A. [Role des anticholinergiques dans la bronchiolite aigue du nourisson]. Archives de Pédiatrie 1995;2(Suppl 2):159‐62. - PubMed
Modaressi 2012 {published data only}
Modl 2005 {published data only}
-
- Modl M, Eber E, Malle‐Scheid D, Weinhandl E, Zach MS. Does bronchodilator responsiveness in infants with bronchiolitis depend on age?. Journal of Pediatrics 2005;147(5):617‐21. - PubMed
Mull 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mull CC, Scarfone RJ, Ferri LR, Carlin T, Salvaggio C, Bechtel KA, et al. A randomized trial of nebulized epinephrine vs albuterol in the emergency department treatment of bronchiolitis. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2004;158(2):113‐8. - PubMed
Ndrepepa 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ndrepepa A, Sinamti J, Vevcka E, Kote L. Comparative study of inhaled bronchodilators in infants less than 18 months old with acute bronchiolitis. European Respiratory Journal 1998;12(Suppl 28):4085.
Numa 2001 {published data only}
-
- Numa AH, Williams GD, Dakin CJ. The effect of nebulized epinephrine on respiratory mechanics and gas exchange in bronchiolitis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2001;164(1):86‐91. - PubMed
Ozyurek 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ozyurek H, Uyan AP, Keskin M, Afsar Y, Kocabay K. Comparison of two different bronchodilators in the treatment of acute bronchiolitis. Cocuk Sagligi ve Hastaliklari Dergisi 2002;45(4):298‐303.
Ralston 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ralston S, Roohi M. A randomized, controlled trial of nasal phenylephrine in infants hospitalized for bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 2008;153:795‐8. - PubMed
Ray 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ray MS, Singh V. Comparison of nebulized adrenaline versus salbutamol in wheeze associated respiratory tract infection in infants. Indian Pediatrics 2002;39:12‐22. - PubMed
Reijonen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Reijonen T, Korppi M, Pitkakangas S, Tenhola S, Remes K. The clinical efficacy of nebulized racemic epinephrine and albuterol in acute bronchiolitis. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 1995;149:686‐92. - PubMed
Ren 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ren CL, Scarlett EE. Effect of inhaled albuterol on tidal breathing patterns in infants hospitalized for viral bronchiolitis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2011;183:A1889. [DOI: 10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2011.183.1_MeetingAbstracts.A1889A1889] - DOI
Sanchez 1993 {published data only}
-
- Sanchez I, Koster J, Powell RE, Wolstein R, Chernick V. Effect of racemic epinephrine and salbutamol on clinical score and pulmonary mechanics in infants with bronchiolitis. Journal of Pediatrics 1993;122:145‐51. - PubMed
Sarrell 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sarrell EM, Tal G, Witzling M, Someck E, Houri S, Cohen HA, et al. Nebulized 3% hypertonic saline solution treatment in ambulatory children with viral bronchiolitis decreases symptoms. Chest 2002;122:2015‐20. - PubMed
Schuh 1992 {published data only}
-
- Schuh S, Johnson D, Canny G, Reisman J, Shields M, Kovesi T, et al. Efficacy of adding nebulized ipratropium bromide to nebulized albuterol therapy in acute bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 1992;90:920‐3. - PubMed
Sezer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sezer GR, Bozaykut A, Ipek IO, Uyur E, Seren PL, Paketci C. The efficacy of nebulized salbutamol, hypertonic saline and salbutamol/hypertonic saline combination in first bronchiolitis attack. Acta Paediatrica, International Journal of Paediatrics 2010;99:114.
Sharma 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sharma BS, Gupta MK, Rafik SP. Hypertonic (3%) saline vs 0.9% saline nebulization for acute viral bronchiolitis: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatrics 2013;50(14):743‐7. - PubMed
Shu 2001 {published data only}
-
- Shu L, Long Z, Pi GX. Therapeutic effect of ipratropine combined with heparin aerosol inhalation on children with bronchiolitis. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics 2001;3(5):555‐6.
Simsek 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Simsek PO, Aslan AT, Kiper N, Yalcin E, Dogru D, Ozcelic U, et al. A randomized trial of the effectiveness of nebulized therapy with epinephrine compared with salbutamol in the treatment of acute viral bronchiolitis [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. 18 September 2005:Poster P865.
Simsek‐Kiper 2011 {published data only}
-
- Simsek‐Kiper PO, Kiper N, Hascelik G, Dolgun A, Yalcin E, Dogru‐Ersoz D, et al. Emergency room management of acute bronchiolitis: a randomized trial of nebulized epinephrine. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2011;6:651‐60. - PubMed
Sly 1991 {published data only}
-
- Sly PD, Lanteri CJ, Raven JM. Do wheezy infants recovering from bronchiolitis respond to inhaled salbutamol?. Pediatric Pulmonology 1991;10:36‐9. - PubMed
Soto 1985 {published data only}
-
- Soto ME, Sly PD, Uren E, Taussig LM, Landau LI. Bronchodilator response during acute viral bronchiolitis in infancy. Pediatric Pulmonology 1985;1(2):85‐90. - PubMed
Springer 1990 {published data only}
-
- Springer C, Bar‐Yishay E, Uwayyed K, Avital A, Vilozni D, Godfrey S. Corticosteroids do not affect the clinical or physiological status of infants with bronchiolitis. Pediatric Pulmonology 1990;9:181‐5. - PubMed
Stokes 1983 {published data only}
Tatochenko 1988 {published data only}
-
- Tatochenko VK, Shiryaeva IS, Dorokhova NF, et al. Effectiveness of spasmolytic aerosols in infants with obstructive bronchitis. Voprosy Okhrany Materinstva i Detstva 1988;33:31‐3.
Torres 1997 {published data only}
-
- Torres Jr A, Anders M, Anderson P, Heulitt MJ. Efficacy of metered‐dose inhaler administration of albuterol in intubated infants. Chest 1997;112:484‐90. - PubMed
Walsh 2008 {published data only}
Wankum 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wankum P, Graff GR, Tobias J. A comparison of the effects of nebulized albuterol, L‐epinephrine, and saline on the pulmonary mechanics in RSV bronchiolitis [Abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;161(Suppl 3):A340. [CN‐00428970]
Zhen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhen KJ, Xiong MH, Wang JH, Lu XX, Wang WW, Lin RM. Fog‐inhalation therapy of Ventolin for bronchiolitis in babies. Medical Journal of Qilu 2003;18(2):180‐1.
Zhou 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zhou XH, Lu M. Clinical outcomes observation of inspiring budesonide and salbutamol on children bronchiolitis. Journal of Nanjing Railway Medical College 2001;20(2):120‐1.
Additional references
AAP 2006
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Management of Bronchiolitis. Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 2006;118:1774‐93. - PubMed
Babl 2008
-
- Babl FE, Sheriff N, Neutze J, Borland M, Oakley E. Bronchiolitis management in pediatric emergency departments in Australia and New Zealand: a PREDICT study. Pediatric Emergency Care 2008;24(10):656‐8. - PubMed
Barben 2003
-
- Barben J, Hammer J. Current management of acute bronchiolitis in Switzerland. Swiss Medical Weekly 2003;133(1‐2):9‐15. - PubMed
Bracken 1989
-
- Bracken MB. Statistical methods for analysis of effects of treatment in overviews of randomized trials. In: Chalmers I, Enkin M, Keirse MJNC editor(s). Effective Care in Pregnancy and Childbirth. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1989:13‐8.
CCHMC 2010
-
- Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC). Evidence‐based care guideline for management of first time episode bronchiolitis in infants less than 1 year of age. Cincinnati (OH): Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center 2010:16.
Chavasse 2002
Christakis 2005
-
- Christakis DA, Cowan CA, Garrison MM, Molteni R, Marcuse E, Zerr DM. Variation in inpatient diagnostic testing and management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 2005;115(4):878‐84. - PubMed
Cruz 1995
-
- Cruz MN, Stewart G, Rosenberg N. Use of dexamethasone in the outpatient management of acute laryngotracheitis. Pediatrics 1995;96:220‐3. - PubMed
de Bilderling 2003
-
- Bilderling G, Bodart E. Bronchiolitis management by the Belgian paediatrician: discrepancies between evidence‐based medicine and practice. Acta Clinica Belgica 2003;58(2):98‐105. - PubMed
DeNicola 2013
-
- DeNicola LK. Bronchiolitis treatment & management. Medscape (http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/961963‐treatment) 2013 (accessed 12 September 2013). [Accessed September 12, 2013.http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/961963‐treatment]
Destino 2010
-
- Destino L, Soung P, Weisgerber M, Bakalarski D, Yan K, Rehborg R, et al. The reliability and validity of the respiratory distress assessment instrument (RDAI) and Children's Hospital of Wisconsin Respiratory Score (CHWRS) in infants with bronchiolitis. Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting, Vancouver, Canada; 2010 May 4. 2010:Abstract #4403.187.
Destino 2012
-
- Destino L, Weisgerber MC, Soung P, Bakalarski D, Yan K, Rehborg R, et al. Validity of respiratory scores in bronchiolitis. Hospital Pediatrics 2012;2(4):202‐9. - PubMed
Disney 1960
Flores 1997
-
- Flores G, Horwitz RI. Efficacy of beta2‐agonists in bronchiolitis: a reappraisal and meta‐analysis. Pediatrics 1997;100:233‐9. - PubMed
Florin 2013
-
- Florin TA, Byczkowski T, Ruddy R, Zorc J, Test M, Sha SS. Variation in the management of infants hospitalized for bronchiolitis persists after the 2006 AAP Bronchiolitis Guidelines. Pediatrics Academic Societies Meeting. 2013:Abstract 1150.5.
Goodman 1993
-
- Goodman BT, Chambers TL. Bronchodilators for bronchiolitis?. Lancet 1993;341:1380. - PubMed
Guia Salud 2010
-
- Giua Salud. Clinical practice guideline on acute bronchiolitis. Catalan Agency for Health Information, Assessment and Quality ‐ State/Local Government Agency [Non‐U.S.] 2010.
Hall 2004
-
- Hall CB. Managing bronchiolitis and respiratory syncytial virus. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2004;158:111‐2. - PubMed
Hall 2007
-
- Hall CB. Therapy for bronchiolitis: when some becomes none. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357(4):402‐4. - PubMed
Hall 2009
Hall 2013
-
- Hall CB, Weinberg GA, Blumkin AK, Edwards KM, Staat MA, Schultz AF, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus‐associated hospitalizations among children less than 24 months of age. Pediatrics 2013;132(2):e341‐8. - PubMed
Hariprakash 2003
-
- Hariprakash S, Alexander J, Carroll W, Ramesh P, Randell T, Turnbull F, et al. Randomized controlled trial of nebulized adrenaline in acute bronchiolitis. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2003;14:134‐9. - PubMed
Hartling 2003
-
- Hartling L, Wiebe N, Russell K, Patel H, Klassen TP. A meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials evaluating the efficacy of epinephrine for the treatment of acute viral bronchiolitis. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(10):957‐64. - PubMed
Hartling 2011a
Hartling 2011b
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester: Wiley‐Blackwell, 2011.
Johnson 2013
-
- Johnson LW, Robles J, Hudgins A, Osburn S, Martin D, Thompson A. Management of bronchiolitis in the emergency department: impact of evidence‐based guidelines?. Pediatrics 2013;131(Suppl 1):103‐9. - PubMed
King 2004
-
- King VJ, Viswanathan M, Bordley C, Jackman AM, Sutton SF, Lohr KN, et al. Pharmacologic treatment of bronchiolitis in infants and children. A systematic review. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2004;158:127‐37. - PubMed
Kristjánsson 1993
La Via 1992
-
- Via WV, Marks MI, Stutman HR. Respiratory syncytial virus puzzle: clinical features, pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;121:503‐10. - PubMed
Langley 2003
-
- Langley JM, LeBlanc JC, Smith B, Wang EE. Increasing incidence of hospitalization for bronchiolitis among Canadian children, 1980‐2000. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2003;188(11):1764‐7. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester: Wiley‐Blackwell, 2011.
Levison 1991
Lowell 1987
-
- Lowell DI, Lister G, Koss H, McCarthy P. Wheezing in infants: the response to epinephrine. Pediatrics 1987;79:939‐45. - PubMed
McCallum 2013
-
- McCallum GB, Morris PS, Wilson CC, Versteegh LA, Ward LM, Chatfield MD, et al. Severity scoring systems: are they internally valid, reliable and predictive of oxygen use in children with acute bronchiolitis?. Pediatric Pulmonology 2013;48(8):797‐803. - PubMed
Nair 2010
Paramore 2004
-
- Paramore LC, Ciuryla V, Ciesla G, Liu L. Economic impact of respiratory syncytial virus‐related illness in the US: an analysis of national databases. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22:275‐84. - PubMed
Plint 2004
-
- Plint AC, Johnson DW, Wiebe N, Bulloch B, Pusic M, Joubert G, et al. Practice variation among pediatric emergency departments in the treatment of bronchiolitis. Academic Emergency Medicine 2004;11(4):353‐60. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Shay 1999
-
- Shay DK, Holman RC, Newman RD, Liu LL, Stout JW, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis‐associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980‐1996. JAMA 1999;282(15):1440‐6. - PubMed
Shay 2001
-
- Shay DK, Holman RC, Roosevelt GE, Clarke MJ, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis‐associated mortality and estimates of respiratory syncytial virus‐associated deaths among US children, 1979‐1997. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2001;183(1):16‐22. - PubMed
SIGN 2006
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Bronchiolitis in children. A national clinical guideline. Edinburgh (Scotland): Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). SIGN publication 2006;91:41.
Thompson 1991
-
- Thompson SG, Pocock SJ. Can meta‐analyses be trusted?. Lancet 1991;338:1127‐30. - PubMed
Thompson 1994
Vogel 2003
-
- Vogel AM, Lennon DR, Harding JE, Pinnock RE, Graham DA, Grimwood K, et al. Variations in bronchiolitis management between five New Zealand hospitals: can we do better?. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2003;39(1):40‐5. - PubMed
Wagner 2009
-
- Wagner T. Bronchiolitis. Pediatrics in Review 2009;30(10):386‐95. - PubMed
Wainwright 2003
-
- Wainwright C, Altamirano L, Cheney M, Cheney J, Barber S, Price D. A multicenter, randomized, double blind, controlled trial of nebulized epinephrine in infants with acute bronchiolitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;349(1):27‐35. - PubMed
Wainwright 2010
Wang 1996
-
- Wang EE, Law BJ, Boucher FD, Stephens D, Robinson JL, Dobson S, et al. Pediatric Investigators Collaborative Network in Infections in Canada (PICNIC) study of admissions and management variation in patients hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;1996:390‐5. - PubMed
Welliver 1992
-
- Welliver RC, Cherry JD. Bronchiolitis and infectious asthma. In: Feigin RD, Cherry JD editor(s). Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Third Edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1992:245‐54.
Wilson 2001
-
- Wilson DF, Horn SD, Hendley JO, Smout R, Gassaway J. Effect of practice variation on resource utilization in infants hospitalized for viral lower respiratory illness. Pediatrics 2001;108:851‐5. - PubMed
Wilson 2010
-
- Wilson KM, Blumkin AK, Rauch DA, Szilagyi PG. Trends in cost and length of stay for children hospitalized for bronchiolitis: 2000‐2006. Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting; 2010 May 2; Vancouver, Canada.
Zorc 2010
-
- Zorc JJ, Hall CB. Bronchiolitis: recent evidence on diagnosis and management. Pediatrics 2010;125(2):342‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Gadomski 2006
Gadomski 2010
Kellner 1996
-
- Kellner JD, Ohlsson A, Gadomski AM, Wang EEL. Efficacy of bronchodilator therapy in bronchiolitis: a meta‐analysis. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 1996;150:1166‐72. - PubMed
Kellner 1998
-
- Kellner JD, Ohlsson A, Gadomski AM, Wang EEL. Bronchodilator therapy in bronchiolitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1998, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001266.pub2] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

