Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 24937669
- PMCID: PMC4102934
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.199
Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation (TACE) is the treatment of choice for intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Doxorubicin-loaded drug-eluting beads (DEB)-TACE is expected to improve the performance of conventional TACE (cTACE). The aim of this study was to compare DEB-TACE with cTACE in terms of time-to-tumour progression (TTP), adverse events (AEs), and 2-year survival.
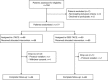
Methods: Patients were randomised one-to-one to undergo cTACE or DEB-TACE and followed-up for at least 2 years or until death. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation was repeated 'on-demand'.
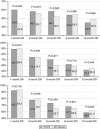
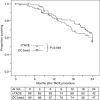
Results: We enrolled 177 patients: 89 underwent DEB-TACE and 88 cTACE. The median number of procedures was 2 in each arm, and the in-hospital stay was 3 and 4 days, respectively (P=0.323). No differences were found in local and overall tumour response. The median TTP was 9 months in both arms. The AE incidence and severity did not differ between the arms, except for post-procedural pain, more frequent and severe after cTACE (P<0.001). The 1- and 2-year survival rates were 86.2% and 56.8% after DEB-TACE and 83.5% and 55.4% after cTACE (P=0.949). Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG), serum albumin, and tumour number independently predicted survival (P<0.05).
Conclusions: The DEB-TACE and the cTACE are equally effective and safe, with the only advantage of DEB-TACE being less post-procedural abdominal pain.
Figures

References
-
- Bolondi L, Cillo U, Colombo M, Craxì A, Farinati F, Giannini EG, Golfieri R, Levrero M, Pinna AD, Piscaglia F, Raimondo G, Trevisani F, Bruno R, Caraceni P, Ciancio A, Coco B, Fraquelli M, Rendina M, Squadrito G, Toniutto P. Position paper of the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF): The multidisciplinary clinical approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45:712–723. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35:519–524. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sherman M. Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42:1208–1236. - PubMed
-
- Burnand B, Kernan WN, Feinstein AR. Indexes and boundaries for "quantitative significance" in statistical decisions. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43:1273–1284. - PubMed
-
- Burrel M, Reig M, Forner A, Barrufet M, de Lope CR, Tremosini S, Ayuso C, Llovet JM, Real MI, Bruix J. Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) using Drug Eluting Beads. Implications for clinical practice and trial design. J Hepatol. 2012;56:1330–1335. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

