IgG, IgM and IgA antibodies against the novel polyprotein in active tuberculosis
- PMID: 24939009
- PMCID: PMC4071025
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-336
IgG, IgM and IgA antibodies against the novel polyprotein in active tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: The present study was aimed to evaluate whether IgG, IgM and IgA antibodies levels detected against a novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis polyprotein 38 F-64 F (with 38 F being the abbreviation for 38kD-ESAT6-CFP10 and 64 F for Mtb8.4-MPT64-TB16.3-Mtb8) are suitable for diagnosing active tuberculosis, and for monitoring the efficacy of chemotherapy on TB patients.
Methods: In this study, a total of 371 active TB patients without treatment were selected and categorized into S+/C+group (n=143), S-/C+group (n=106) or S-/C- group (n=122). A series of serum samples were collected from 82 active TB patients who had undergone anti-TB chemotherapy for 0-6 months at one month interval. Humoral responses (IgG, IgM and IgA) were determined for the novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis polyprotein using indirect ELISA methods in all of serum samples.
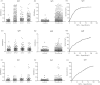
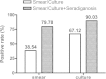
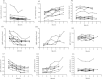
Results: For S+/C+, S-/C+and S-/C- active tuberculosis patients before anti-TB chemotherapy, the sensitivities of tests based on IgG were 65.7%, 46.2% and 52.5% respectively; the sensitivities based on IgM were 21.7%, 24.5% and 18.9%; and the sensitivities based on IgA were 25.2%, 17.9% and 23.8%. By combination of three isotypes, for all active tuberculosis patients, the test sensitivity increased to 70.4% with the specificity being 91.5%. After anti-TB chemotherapy, there were no significant differences between groups with different courses of anti-TB chemotherapy.
Conclusions: The novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis polyprotein 38 F-64 F represents potential antigen suitable for measuring IgG, IgM and IgA antibodies. However, the serodiagnostic test based on the 38 F-64 F polyprotein appears unsuitable for monitoring the efficacy of chemotherapy.
Figures
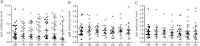
References
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis control. Geneva: Switzerland; 2010.
-
- Ai-Zamel FA. Detection and diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009;14:1099–1108. - PubMed
-
- Wallis RS, Pai M, Menzies D, Doherty TM, Walzl G, Perkins MD, Zumla A. Biomarkers and diagnostics for tuberculosis: progress, needs, and translation into practice. Lancet. 2010;14:1920–1937. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. Center for Disease Control and Prevention: Diagnostic standards and classification of tuberculosis in adults and children . Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;14:1376–1395. - PubMed
-
- Teixeira HC, Abramo C, Munk ME. Immunological diagnosis of tuberculosis: problems and strategies for success. J Bras Pneumol. 2007;14:323–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

