Hospital variation in survival after pediatric in-hospital cardiac arrest
- PMID: 24939940
- PMCID: PMC4276414
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.113.000691
Hospital variation in survival after pediatric in-hospital cardiac arrest
Abstract
Background: Although survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest is likely to vary among hospitals caring for children,validated methods to risk-standardize pediatric survival rates across sites do not currently exist.
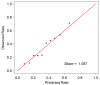
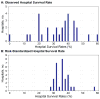
Methods and results: From 2006 to 2010, within the American Heart Association's Get With the Guidelines-Resuscitation registry for in-hospital cardiac arrest, we identified 1551 cardiac arrests in children (<18 years). Using multivariable hierarchical logistic regression, we developed and validated a model to predict survival to hospital discharge and calculated risk-standardized rates of cardiac arrest survival for hospitals with a minimum of 10 pediatric cardiac arrest cases. A total of 13 patient-level predictors were identified: age, sex, cardiac arrest rhythm, location of arrest, mechanical ventilation, acute nonstroke neurological event, major trauma, hypotension, metabolic or electrolyte abnormalities, renal insufficiency, sepsis, illness category, and need for intravenous vasoactive agents prior to the arrest. The model had good discrimination (C-statistic of 0.71), confirmed by bootstrap validation (validation C-statistic of 0.69). Among 30 hospitals with ≥10 cardiac arrests, unadjusted hospital survival rates varied considerably (median, 37%; interquartile range, 24-42%; range, 0-61%). After risk-standardization, the range of hospital survival rates narrowed (median, 37%; interquartile range, 33-38%; range, 29-48%), but variation in survival persisted.
Conclusions: Using a national registry, we developed and validated a model to predict survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest in children. After risk-standardization, significant variation in survival rates across hospitals remained. Leveraging these models, future studies can identify best practices at high-performing hospitals to improve survival outcomes for pediatric cardiac arrest. (
Figures
References
-
- Matos RI, Watson RS, Nadkarni VM, Huang HH, Berg RA, Meaney PA, Carroll CL, Berens RJ, Praestgaard A, Weissfeld L, Spinella PC. Duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and illness category impact survival and neurologic outcomes for in-hospital pediatric cardiac arrests. Circulation. 2013;127:442–451. - PubMed
-
- Krumholz HM, Brindis RG, Brush JE, Cohen DJ, Epstein AJ, Furie K, Howard G, Peterson ED, Rathore SS, Smith SC, Jr, Spertus JA, Wang Y, Normand SL. Standards for statistical models used for public reporting of health outcomes: An American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Writing Group: Cosponsored by the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention and the Stroke Council. Endorsed by the American College of Cardiology Foundation. Circulation. 2006;113:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Peberdy MA, Kaye W, Ornato JP, Larkin GL, Nadkarni V, Mancini ME, Berg RA, Nichol G, Lane-Trultt T. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of adults in the hospital: A report of 14720 cardiac arrests from the National Registry of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2003;58:297–308. - PubMed
-
- Cummins RO, Chamberlain D, Hazinski MF, Nadkarni V, Kloeck W, Kramer E, Becker L, Robertson C, Koster R, Zaritsky A, Bossaert L, Ornato JP, Callanan V, Allen M, Steen P, Connolly B, Sanders A, Idris A, Cobbe S. Recommended guidelines for reviewing, reporting, and conducting research on in-hospital resuscitation: The in-hospital ‘Utstein style’. American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997;95:2213–2239. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs I, Nadkarni V, Bahr J, Berg RA, Billi JE, Bossaert L, Cassan P, Coovadia A, D’Este K, Finn J, Halperin H, Handley A, Herlitz J, Hickey R, Idris A, Kloeck W, Larkin GL, Mancini ME, Mason P, Mears G, Monsieurs K, Montgomery W, Morley P, Nichol G, Nolan J, Okada K, Perlman J, Shuster M, Steen PA, Sterz F, Tibballs J, Timerman S, Truitt T, Zideman D. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: Update and simplification of the Utstein templates for resuscitation registries: A statement for healthcare professionals from a task force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian Resuscitation Council, New Zealand Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Interamerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Councils of Southern Africa) Circulation. 2004;110:3385–3397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical