Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy: the path to consensus on pathophysiology
- PMID: 24940479
- PMCID: PMC4060068
- DOI: 10.1186/2044-5040-4-12
Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy: the path to consensus on pathophysiology
Abstract
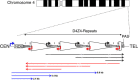
Although the pathophysiology of facioscapulohumeral dystrophy (FSHD) has been controversial over the last decades, progress in recent years has led to a model that incorporates these decades of findings and is gaining general acceptance in the FSHD research community. Here we review how the contributions from many labs over many years led to an understanding of a fundamentally new mechanism of human disease. FSHD is caused by inefficient repeat-mediated epigenetic repression of the D4Z4 macrosatellite repeat array on chromosome 4, resulting in the variegated expression of the DUX4 retrogene, encoding a double-homeobox transcription factor, in skeletal muscle. Normally expressed in the testis and epigenetically repressed in somatic tissues, DUX4 expression in skeletal muscle induces expression of many germline, stem cell, and other genes that might account for the pathophysiology of FSHD. Although some disagreements regarding the details of mechanisms remain in the field, the coalescing agreement on a central model of pathophysiology represents a pivot-point in FSHD research, transitioning the field from discovery-oriented studies to translational studies aimed at developing therapies based on a sound model of disease pathophysiology.
Keywords: DUX4; Epigenetic; Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy; SMCHD1; Tandem repeat sequences.
Figures

References
-
- Landouzy L, Dejerine J. De la myopathie atrophique progressive. Rev Med Franc. 1885;5:81–253.
-
- Tyler FH, Stephens FE. Studies in disorders of muscle. II Clinical manifestations and inheritance of facioscapulohumeral dystrophy in a large family. Ann Intern Med. 1950;32:640–660. - PubMed
-
- Lemmers RJ, Tawil R, Petek LM, Balog J, Block GJ, Santen GW, Amell AM, van der Vliet PJ, Almomani R, Straasheijm KR, Krom YD, Klooster R, Sun Y, den Dunnen JT, Helmer Q, Donlin-Smith CM, Padberg GW, van Engelen BG, de Greef JC, Aartsma-Rus AM, Frants RR, de Visser M, Desnuelle C, Sacconi S, Filippova GN, Bakker B, Bamshad MJ, Tapscott SJ, Miller DG, van der Maarel SM. Digenic inheritance of an SMCHD1 mutation and an FSHD-permissive D4Z4 allele causes facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy type 2. Nat Genet. 2012;44:1370–1374. doi: 10.1038/ng.2454. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Greef JC, Lemmers RJ, Camano P, Day JW, Sacconi S, Dunand M, van Engelen BG, Kiuru-Enari S, Padberg GW, Rosa AL, Desnuelle C, Spuler S, Tarnopolsky M, Venance SL, Frants RR, van der Maarel SM, Tawil R. Clinical features of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy 2. Neurology. 2010;75:1548–1554. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f96175. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

