HBx induces hypomethylation of distal intragenic CpG islands required for active expression of developmental regulators
- PMID: 24941955
- PMCID: PMC4084425
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1400604111
HBx induces hypomethylation of distal intragenic CpG islands required for active expression of developmental regulators
Abstract
Epigenetic alterations caused by viral oncoproteins are strong initiation factors for cancer development, but their mechanisms are largely unknown. To identify the epigenetic effects of viral hepatitis B virus X (HBx) that lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), we profiled the DNA methylomes of normal and HBx transgenic mouse liver. Intriguingly, severe hypomethylation of intragenic CpG islands (CGIs) was observed in HBx liver before the full development of HCC. Normally, these CGIs were highly methylated (mCGIs) by the DNMT3L complex and marked with epigenetic signatures associated with active expression, such as H3K36me3. Hypomethylation of mCGI was caused by the downregulation of Dnmt3L and Dnmt3a due to HBx bound to their promoters, along with HDAC1. These events lead to the downregulation of many developmental regulators that could facilitate tumorigenesis. Here we provide an intriguing epigenetic regulation mediated by mCGI that is required for cell differentiation and describe a previously unidentified epigenetic role for HBx in promoting HCC development.
Keywords: DNA methylation; methylated CpG island; viral protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

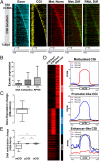
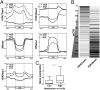

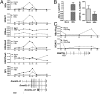
References
-
- Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(9):674–687. - PubMed
-
- Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 2004;11(2):97–107. - PubMed
-
- Bowen DG, Walker CM. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature. 2005;436(7053):946–952. - PubMed
-
- Rapicetta M, Ferrari C, Levrero M. Viral determinants and host immune responses in the pathogenesis of HBV infection. J Med Virol. 2002;67(3):454–457. - PubMed
-
- Sung WK, et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2012;44(7):765–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

