Ibrutinib: a first in class covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 24941982
- PMCID: PMC4632638
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.14.51
Ibrutinib: a first in class covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase
Abstract
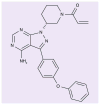
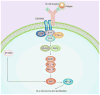
Ibrutinib (formerly PCI-32765) is a potent, covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase, a kinase downstream of the B-cell receptor that is critical for B-cell survival and proliferation. In preclinical studies, ibrutinib bound to Bruton's tyrosine kinase with high affinity, leading to inhibition of B-cell receptor signaling, decreased B-cell activation and induction of apoptosis. In clinical studies, ibrutinib has been well-tolerated and has demonstrated profound anti-tumor activity in a variety of hematologic malignancies, most notably chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), leading to US FDA approval for relapsed CLL and MCL. Ongoing studies are evaluating ibrutinib in other types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Waldenström's macrogobulinemia, in larger Phase III studies in CLL and MCL, and in combination studies with monoclonal antibodies and chemotherapy. Future studies will combine ibrutinib with other promising novel agents currently in development in hematologic malignancies.
Keywords: B-cell receptor; BTK; CLL; MCL; NHL; ibrutinib; kinase; lymphocytosis.
Figures
References
-
- de Weers M, Mensink RG, Kraakman ME, Schuurman RK, Hendriks RW. Mutation analysis of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase gene in X-linked agammaglobulinemia: identification of a mutation which affects the same codon as is altered in immunodeficient xid mice. Hum Mol Genet. 1994;3(1):161–166. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, Phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164–1174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous