Enterovirus 71 3C inhibits cytokine expression through cleavage of the TAK1/TAB1/TAB2/TAB3 complex
- PMID: 24942571
- PMCID: PMC4136319
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01425-14
Enterovirus 71 3C inhibits cytokine expression through cleavage of the TAK1/TAB1/TAB2/TAB3 complex
Abstract
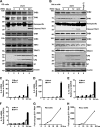
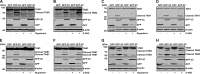
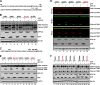
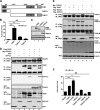
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) causes hand, foot, and mouth disease in young children and infants. Severe infection with EV71 can lead to various neurological complications or fatal diseases. However, the mechanism of EV71 pathogenesis is poorly understood. Emerging evidence suggests that EV71 modulates type I interferon (IFN) and cytokine responses. Here, we show that EV71 disables components of the TAB2 complex through the 3C protein. When expressed in mammalian cells, EV71 3C interacts with TAB2 and TAK1, which inhibits NF-κB activation. Furthermore, 3C mediates cleavage of TAB2 and its partners, which requires the protease activity. H40D or C147S substitution in the 3C active sites abolishes its activity, whereas R84Q or V154S substitution in the RNA binding domain has no effect. The 3C protein targets TAB2 at Q113-S114, TAK1 at Q360-S361, TAB1 both at Q414-G415 and Q451-S452, and TAB3 at Q173-G174 and Q343-G344. Importantly, overexpression of TAB2 inhibits EV71 replication, whereas addition of cleaved fragments has no effect. Thus, an equilibrium between the TAB2 complex and EV71 3C represents a control point of viral infection. These results suggest that TAK1/TAB1/TAB2/TAB3 cleavage mediated by EV71 may be a mechanism to interfere with inflammatory responses.
Importance: The TAK1 complex plays a critical role in the activation of NF-κB and cytokine production. However, little is known about its connection to enterovirus 71 (EV71). We demonstrate that EV71 3C suppresses cytokine expression via cleavage of the TAK1 complex proteins. EV71 3C interacts with TAB2 and TAK1. Furthermore, overexpression of TAB2 inhibits EV71 replication, whereas addition of cleaved fragment has no effect. These results suggest that the interplay of EV71 and the TAK1 complex influences the outcome of viral infection.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cleavage of interferon regulatory factor 7 by enterovirus 71 3C suppresses cellular responses.J Virol. 2013 Feb;87(3):1690-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01855-12. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23175366 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of the adaptor protein TRIF by enterovirus 71 3C inhibits antiviral responses mediated by Toll-like receptor 3.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):8811-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00447-11. Epub 2011 Jun 22. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21697485 Free PMC article.
-
The 3C protein of enterovirus 71 inhibits retinoid acid-inducible gene I-mediated interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and type I interferon responses.J Virol. 2010 Aug;84(16):8051-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02491-09. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20519382 Free PMC article.
-
The Function and Mechanism of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) 3C Protease.Curr Microbiol. 2020 Sep;77(9):1968-1975. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-02082-4. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Curr Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32556480 Review.
-
Post-Translational Modifications of the TAK1-TAB Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 19;18(1):205. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010205. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28106845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the Control of the Life and Death Balance of Macrophages.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 May 29;7:91. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00091. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31192209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple roles of caspase-8 in cell death, inflammation, and innate immunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2021 Jan;109(1):121-141. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MR0420-305R. Epub 2020 Jun 12. J Leukoc Biol. 2021. PMID: 32531842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Pseudophosphatases in Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 28;22(13):6924. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136924. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on Toll-like receptor signal transduction and its roles in antimicrobial immune responses.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul;105(13):5341-5355. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11406-8. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34180006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Virulence Determinant: The 69th Residue of 3C Protease Modulates Pathogenicity.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Feb 3;7:26. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00026. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28217559 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

