Influence of family, friend and coworker social support and social undermining on weight gain prevention among adults
- PMID: 24942930
- PMCID: PMC4435839
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.20814
Influence of family, friend and coworker social support and social undermining on weight gain prevention among adults
Abstract
Objective: Examine longitudinal associations between sources of social support and social undermining for healthy eating and physical activity and weight change.
Methods: Data are from 633 employed adults participating in a cluster-randomized multilevel weight gain prevention intervention. Primary predictors included social support and social undermining for two types of behaviors (healthy eating and physical activity) from three sources (family, friends, and coworkers) obtained via self-administered surveys. The primary outcome (weight in kg) was measured by trained staff. Data were collected at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Linear multivariable models examined the association of support and social undermining with weight over time, adjusting for intervention status, time, gender, age, education, and clustering of individuals within schools.
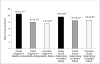
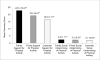
Results: Adjusting for all primary predictors and covariates, friend support for healthy eating (β = -0.15), coworker support for healthy eating (β = -0.11), and family support for physical activity (β = -0.032) were associated with weight reduction at 24 months (P-values<0.05). Family social undermining for healthy eating was associated with weight gain at 24 months (β = 0.12; P = 0.0019).
Conclusions: Among adult employees, friend and coworker support for healthy eating and family support for physical activity predicted improved weight management. Interventions that help adults navigate family social undermining of healthy eating are warranted.
© 2014 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. NCHS data brief, no 82. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2012. Prevalence of obesity in the United States, 2009–2010. - PubMed
-
- Faith MS, Kral TVE. Social Environmental and Genetic Influences on Obesity and Obesity-Promoting Behaviors: Fostering Research Integration. In: Hernandez LM, Blazer DG, editors. Genes, Behavior, and the Social Environment: Moving Beyond the Nature/Nurture Debate. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2006. - PubMed
-
- Christakis NA, Fowler JH. The spread of obesity in a large social network over 32 years. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(4):370–9. - PubMed
-
- Oliveira AJ, Rostila M, de Leon AP, Lopes CS. The influence of social relationships on obesity: sex differences in a longitudinal study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013;21(8):1540–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

