Disruption of astrocyte-vascular coupling and the blood-brain barrier by invading glioma cells
- PMID: 24943270
- PMCID: PMC4127490
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5196
Disruption of astrocyte-vascular coupling and the blood-brain barrier by invading glioma cells
Abstract
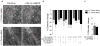
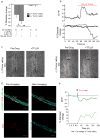
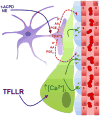
Astrocytic endfeet cover the entire cerebral vasculature and serve as exchange sites for ions, metabolites and energy substrates from the blood to the brain. They maintain endothelial tight junctions that form the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and release vasoactive molecules that regulate vascular tone. Malignant gliomas are highly invasive tumours that use the perivascular space for invasion and co-opt existing vessels as satellite tumour form. Here we use a clinically relevant mouse model of glioma and find that glioma cells, as they populate the perivascular space of preexisting vessels, displace astrocytic endfeet from endothelial or vascular smooth muscle cells. This causes a focal breach in the BBB. Furthermore, astrocyte-mediated gliovascular coupling is lost, and glioma cells seize control over the regulation of vascular tone through Ca(2+)-dependent release of K(+). These findings have important clinical implications regarding blood flow in the tumour-associated brain and the ability to locally deliver chemotherapeutic drugs in disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
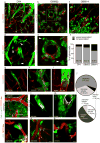
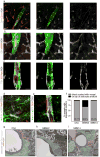
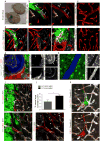

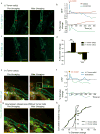
References
-
- Mathiisen TM, Lehre KP, Danbolt NC, Ottersen OP. The perivascular astroglial sheath provides a complete covering of the brain microvessels: an electron microscopic 3D reconstruction. Glia. 2010;58:1094–1103. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1F31NS074597/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057098/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS031234/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS57098/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS048039/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01NS036692/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036692/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS047466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS082851/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS082851/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS074597/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD038985/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS069720/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01NS031234/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM053395/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

