Intrinsically germanium-69-labeled iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and in-vivo dual-modality PET/MR imaging
- PMID: 24944166
- PMCID: PMC4127144
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201401372
Intrinsically germanium-69-labeled iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and in-vivo dual-modality PET/MR imaging
Abstract
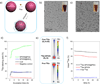
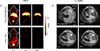
Intrinsically germanium-69-labeled super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are synthesized via a newly developed, fast and highly specific chelator-free approach. The biodistribution pattern and the feasibility of (69) Ge-SPION@PEG for in vivo dual-modality positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance (PET/MR) imaging and lymph-node mapping are investigated, which represents the first example of the successful utilization of a (69) Ge-based agent for PET/MR imaging.
Keywords: chelator-free radiolabeling; germanium-69; iron oxide nanoparticles; multimodality imaging; positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance (PET/MR) imaging.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Mirzadeh S, Lambrecht RM. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1996;202:7.
-
- Park H-J, Tavlarides LL. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009;48:4014.
- Neirinckx RD, Davis MA. J. Nucl. Med. 1979;20:1075. - PubMed
-
- Roesch F, Riss PJ. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010;10:1633. - PubMed
- Chakravarty R, Dash A. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013;13:2431. - PubMed
- Chakravarty R, Shukla R, Ram R, Tyagi AK, Dash A, Venkatesh M. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011;38:575. - PubMed
- Chakravarty R, Shukla R, Ram R, Venkatesh M, Dash A, Tyagi AK. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2010;2:2069. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarty R, Chakraborty S, Ram R, Dash A, Pillai MR. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2013;28:631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

