Differential coupling of KLF10 to Sin3-HDAC and PCAF regulates the inducibility of the FOXP3 gene
- PMID: 24944246
- PMCID: PMC4166759
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00085.2014
Differential coupling of KLF10 to Sin3-HDAC and PCAF regulates the inducibility of the FOXP3 gene
Abstract
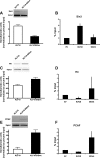
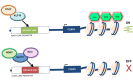
Inducible gene expression, which requires chromatin remodeling on gene promoters, underlies the epigenetically inherited differentiation program of most immune cells. However, chromatin-mediated mechanisms that underlie these events in T regulatory cells remain to be fully characterized. Here, we report that inducibility of FOXP3, a key transcription factor for the development of T regulatory cells, depends upon Kruppel-like factor 10 (KLF10) interacting with two antagonistic histone-modifying systems. We utilized chromatin immunoprecipitation, genome-integrated reporter assays, and functional domain KLF10 mutant proteins, to characterize reciprocal interactions between this transcription factor and either the Sin3-histone deacetylase complex or the histone acetyltransferase, p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF). We characterize a Sin3-interacting repressor domain on the NH2 terminus of KLF10, which works to limit the activating function of this transcription factor. Indeed, inactivation of this Sin3-interacting domain renders KLF10 able to physically associate with PCAF as to induce FOXP3 gene transcription. We show that this biochemical data derived from studying our genome-integrated reporter cell system are recapitulated in primary murine lymphocytes. Collectively, these results advance our understanding of how a single transcription factor, namely KLF10, functions as a toggle to integrate antagonistic signals regulating FOXP3 and, thus, immune activation.
Keywords: FOXP3; KLF10; PCAF; Sin3; T regulatory cell.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 441: 235–238, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Brubaker K, Cowley SM, Huang K, Loo L, Yochum GS, Ayer DE, Eisenman RN, Radhakrishnan I. Solution structure of the interacting domains of the Mad-Sin3 complex: implications for recruitment of a chromatin-modifying complex. Cell 103: 655–665, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

