Prospective evaluation of long-term safety of dual-release hydrocortisone replacement administered once daily in patients with adrenal insufficiency
- PMID: 24944332
- PMCID: PMC4106399
- DOI: 10.1530/EJE-14-0327
Prospective evaluation of long-term safety of dual-release hydrocortisone replacement administered once daily in patients with adrenal insufficiency
Abstract
Objective: The objective was to assess the long-term safety profile of dual-release hydrocortisone (DR-HC) in patients with adrenal insufficiency (AI).
Design: Randomised, open-label, crossover trial of DR-HC or thrice-daily hydrocortisone for 3 months each (stage 1) followed by two consecutive, prospective, open-label studies of DR-HC for 6 months (stage 2) and 18 months (stage 3) at five university clinics in Sweden.
Methods: Sixty-four adults with primary AI started stage 1, and an additional 16 entered stage 3. Patients received DR-HC 20-40 mg once daily and hydrocortisone 20-40 mg divided into three daily doses (stage 1 only). Main outcome measures were adverse events (AEs) and intercurrent illness (self-reported hydrocortisone use during illness).
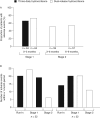
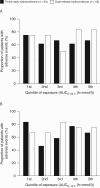
Results: In stage 1, patients had a median 1.5 (range, 1-9) intercurrent illness events with DR-HC and 1.0 (1-8) with thrice-daily hydrocortisone. AEs during stage 1 were not related to the cortisol exposure-time profile. The percentage of patients with one or more AEs during stage 1 (73.4% with DR-HC; 65.6% with thrice-daily hydrocortisone) decreased during stage 2, when all patients received DR-HC (51% in the first 3 months; 54% in the second 3 months). In stages 1-3 combined, 19 patients experienced 27 serious AEs, equating to 18.6 serious AEs/100 patient-years of DR-HC exposure.
Conclusions: This long-term prospective trial is the first to document the safety of DR-HC in patients with primary AI and demonstrates that such treatment is well tolerated during 24 consecutive months of therapy.
© 2014 The authors.
Figures
References
-
- Hahner S, Loeffler M, Bleicken B, Drechsler C, Milovanovic D, Fassnacht M, Ventz M, Quinkler M, Allolio B. Epidemiology of adrenal crisis in chronic adrenal insufficiency: the need for new prevention strategies. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2010;162:597–602. doi: 10.1530/EJE-09-0884. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Erichsen MM, Lovas K, Skinningsrud B, Wolff AB, Undlien DE, Svartberg J, Fougner KJ, Berg TJ, Bollerslev J, Mella B, et al. Clinical, immunological, and genetic features of autoimmune primary adrenal insufficiency: observations from a Norwegian registry. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2009;94:4882–4890. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1368. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mah PM, Jenkins RC, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Newell-Price J, Doane A, Ibbotson V, Tucker GT, Ross RJ. Weight-related dosing, timing and monitoring hydrocortisone replacement therapy in patients with adrenal insufficiency. Clinical Endocrinology. 2004;61:367–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02106.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

