Monoamine neurotransmitters and fibroblast growth factor-2 in the brains of rats with post-stroke depression
- PMID: 24944615
- PMCID: PMC4061212
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1674
Monoamine neurotransmitters and fibroblast growth factor-2 in the brains of rats with post-stroke depression
Abstract
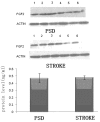
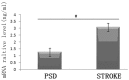
The aim of the present study was to investigate the changes in the levels of serotonin (5-HT), dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) in the brains of rats with post-stroke depression (PSD). A rat model of stroke was established by middle cerebral artery occlusion and the rats were randomly divided into two groups: Control and modification groups. The rats in the modification group had PSD, while the rats in the control group had experienced a stroke only. The PSD model was established by applying chronic mild stress to the individually housed rats. High-performance liquid chromatography was used to detect the levels of 5-HT, DA and NE, while western blotting was used to detect the FGF-2 protein expression levels in the frontal lobe and hippocampus. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction was also used to determine the mRNA expression levels of FGF-2 in the frontal lobes of the two groups. The levels of 5-HT, DA and NE in the frontal lobe and hippocampus of the rats in the PSD group were significantly lower than the levels observed in the rats in the stroke group (P<0.01). In addition, protein expression levels of FGF-2 in the frontal lobe of the rats in the PSD group were significantly lower when compared with the control group rats (P<0.01), however, the protein expression levels of FGF-2 in the hippocampus did not exhibit a statistically significant difference (P>0.05). The mRNA expression levels of FGF-2 in the frontal lobe of the rats in the modification group were significantly lower than the levels in the control group rats (P<0.01). Therefore, reduced levels of monoamine neurotransmitters and FGF-2 expression in the brains of rats with PSD are associated with the incidence of PSD.
Keywords: dopamine; fibroblast growth factor-2; norepinepherine; post-stroke depression rat; serotonin.
Figures

References
-
- Yang LL, Zhang ZJ, Sun DM. Incidence and its risk factors of post-stroke depression in cerebral stroke patients at acute stage. Lin Chuang Shen Jing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2010;23:185–187. (In Chinese)
-
- Spasojevic N, Jovanovic P, Dronjak S. Chronic fluoxetine treatment affects gene expression of catecholamine enzymes in the heart of depression model rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2012;50:771–775. - PubMed
-
- Vergaño-Vera E, Méndez-Gómez HR, Hurtado-Chong A, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 increases the expression of neurogenic genes and promotes the migration and differentiation of neurons derived from transplanted neural stem/progenitor cells. Neuroscience. 2009;162:39–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
