Hypoglycemic and anti-depressant effects of Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu formulation in a model of unpredictable chronic mild stress in rats with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24944635
- PMCID: PMC4061204
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1681
Hypoglycemic and anti-depressant effects of Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu formulation in a model of unpredictable chronic mild stress in rats with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
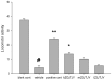
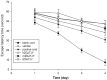
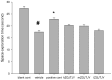
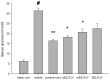
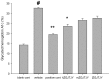
This study aimed to investigate the hypoglycemic, lipid-lowering and antidepressant effects of Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu formulation (ZGJTJY) in a model of unpredictable chronic mild stress (UCMS) in rats with diabetes mellitus (DM; the UCMS-DM model). Sixty rats were randomly divided into blank control, vehicle (model plus vehicle), positive control (model plus metformin and fluoxetine), and high, medium and low dose ZGJTJY (model plus high, medium and low doses of ZGJTJY, respectively) groups. Following establishment of DM by a high-fat diet with intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (38 mg/kg), the depression model was established by application of UCMS for 28 days. The behavioral scores of the rats were detected in an open field test and Morris water maze test. The levels of blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and blood lipids were assayed. The total scores of the open field test and the space exploration times (SETs) in the Morris water maze test were significantly lower and the escape latency (EL) times in the Morris water maze test were significantly longer in the vehicle group compared with those in the blank control group. In addition, in the vehicle group, the levels of blood glucose, HbA1c, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TGs) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were significantly higher and the levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) were significantly lower compared with those in the blank control group. The high dose of ZGJTJY decreased the locomotor activity levels in the open field test, the EL times of the model on day 4, the SETs in the Morris water maze test and the HDL-C levels, and reduced the blood glucose, HbA1c, TC, TG and LDL-C levels compared with those in the model group. Thus, ZGJTJY is a potential candidate for the prevention and treatment of the comorbidity of depression with DM.
Keywords: Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu formulation; diabetes mellitus with depression.
Figures
References
-
- Fujitsuka N, Asakawa A, Hayashi M, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors modify physiological gastrointestinal motor activities via 5-HT2c receptor and acyl ghrelin. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:748–759. - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Ning G, Bloomgarden Z. Diabetes in China: prevalence, diagnosis, and control. J Diabetes. 2013;5:372. - PubMed
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
