Stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally-located lung tumors
- PMID: 24944711
- PMCID: PMC3961379
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.1815
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally-located lung tumors
Abstract
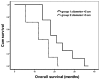
The application of high-dose irradiation to centrally-located lung tumors is generally considered to be of high risk in causing bronchial injury. The aim of the present retrospective study was to investigate the safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for patients with centrally-located lung tumors. In total, 28 patients who underwent SBRT for lung tumors within 2 cm of a major bronchus were retrospectively analyzed. The median total dose prescribed was 45 Gy (range, 36.3-52.5 Gy), the median fraction was 12 (range, 10-15) and the median dose per fraction was 3.6 Gy (range, 3-5 Gy). The median follow-up period for the surviving patients was 14 months (range, 10-41 months). The local control rate of SBRT was 100%, with a complete response (CR) rate of 32.1% (9/28); a partial response (PR) rate of 50% (14/28) and a stable disease (SD) rate of 17.9% (5/28). In total, 15 patients survived and 13 patients succumbed; 11 patients succumbed to tumor progression, one to congestive heart failure and one to a brain hemorrhage. The main side-effects included grade 2 esophagitis (17.9%; 5/28) atelectasis (10.7%; 3/28) and grade 2 late radiation pneumonitis (7.1%; 2/28). Severe late toxicity (≥ grade 3) was not observed in any patient. SBRT is an effective and safe therapy for centrally-located lung tumors.
Keywords: centrally-located; lung tumor; stereotactic body radiation therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Xia T, Li H, Sun Q, Wang Y, Fan N, Yu Y, Li P, Chang JY. Promising clinical outcome of stereotactic body radiation therapy for patients with inoperable Stage I/II non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Haasbeek CJ, Senan S, Smit EF, Paul MA, Slotman BJ, Lagerwaard FJ. Critical review of nonsurgical treatment options for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 2008;13:309–319. - PubMed
-
- Chi A, Liao Z, Nguyen NP, Xu J, Stea B, Komaki R. Systemic review of the patterns of failure following stereotactic body radiation therapy in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: clinical implications. Radiother Oncol. 2010;94:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Palma D, Senan S. Stereotactic radiation therapy: changing treatment paradigms for stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2011;23:133–139. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
