Synthesis of [(11)C]Bexarotene by Cu-Mediated [(11)C]Carbon Dioxide Fixation and Preliminary PET Imaging
- PMID: 24944741
- PMCID: PMC4060930
- DOI: 10.1021/ml500065q
Synthesis of [(11)C]Bexarotene by Cu-Mediated [(11)C]Carbon Dioxide Fixation and Preliminary PET Imaging
Abstract
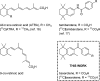
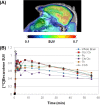
Bexarotene (Targretin) is a retinoid X receptor (RXR) agonist that has applications for treatment of T cell lymphoma and proposed mechanisms of action in Alzheimer's disease that have been the subject of recent controversy. Carbon-11 labeled bexarotene ([(11)C-carbonyl]4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyltetralin-2-yl)ethenyl]benzoic acid) was synthesized using a Cu-mediated cross-coupling reaction employing an arylboronate precursor 1 and [(11)C]carbon dioxide under atmospheric pressure in 15 ± 2% uncorrected radiochemical yield (n = 3), based on [(11)C]CO2. Judicious choice of solvents, catalysts, and additives, as well as precursor concentration and purity of [(11)C]CO2, enabled the preparation of this (11)C-labeled carboxylic acid. Formulated [(11)C]bexarotene was isolated (>37 mCi) with >99% radiochemical purity in 32 min. Preliminary positron emission tomography-magnetic resonance imaging revealed rapid brain uptake in nonhuman primate in the first 75 s following intravenous administration of the radiotracer (specific activity >0.3 Ci/μmol at time of injection), followed by slow clearance (Δ = -43%) over 60 min. Modest uptake (SUVmax = 0.8) was observed in whole brain and regions with high RXR expression.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Bexarotene; carbon dioxide fixation; carbon-11; positron emission tomography; retinoid X receptor; targretin.
Figures
References
-
- Moreno S.; Farioli-Vecchioli S.; Cerù M. P. Immunolocalization of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors and Retinoid X Receptors in the Adult Rat CNS. Neuroscience 2004, 123, 131–145. - PubMed
-
- Boehm M. F.; Zhang L.; Badea B. A.; White S. K.; Mais D. E.; Berger E.; Suto C. M.; Goldman M. E.; Heyman R. A. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationships of Novel Retinoid X Receptor-Selective Retinoids. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2930–2941. - PubMed
-
- Cramer P. E.; Cirrito J. R.; Wesson D. W.; Lee C. Y. D.; Karlo J. C.; Zinn A. E.; Casali B. T.; Restivo J. L.; Goebel W. D.; James M. J.; Brunden K. R.; Wilson D. A.; Landreth G. E. ApoE-Directed Therapeutics Rapidly Clear β-Amyloid and Reverse Deficits in AD Mouse Models. Science 2012, 335, 1503–1506. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

