Effects of chronic leptin infusion on subsequent body weight and composition in mice: Can body weight set point be reset?
- PMID: 24944902
- PMCID: PMC4060284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.02.003
Effects of chronic leptin infusion on subsequent body weight and composition in mice: Can body weight set point be reset?
Abstract
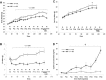
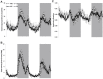
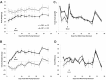
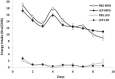
Circulating leptin concentrations correlate with fat mass and signal the status of somatic energy stores to the brain. Previous studies suggest that diet-induced elevations of body weight increase body weight "set-point". To assess whether chronic hyperleptinemia is responsible for this shift in defended body weight, we elevated circulating leptin concentrations in lean mice to those comparable to diet-induced obese mice for eighteen weeks. We hypothesized that following cessation of leptin infusion, a higher body weight would be defended. Compared to saline-infused controls, leptin-infused mice had elevated circulating leptin concentrations, gained less weight, yet had similar metabolic rates. Following cessation of leptin administration, leptin-infused mice gained some weight yet plateaued at 5-10% below controls. These results suggest that, unlike mice rendered hyperleptinemic by diet-induced weight gain, leptin-infused mice do not subsequently "defend" a higher body weight, suggesting that hyperleptinemia per se does not mimic the CNS consequences of chronic weight gain.
Keywords: Body weight “set-point”; Leptin; Leptin resistance; Obesity.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenbaum M., Nicolson M., Hirsch J., Heymsfield S.B., Gallagher D., Chu F. Effects of gender, body composition, and menopause on plasma concentrations of leptin. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1996;81(9):3424–3427. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum M., Leibel R.L. Leptin: a molecule integrating somatic energy stores, energy expenditure and fertility. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1998;9(3):117–124. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

