Diagnosis, causes and treatments of instability following total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 24944970
- PMCID: PMC4061408
- DOI: 10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.2.61
Diagnosis, causes and treatments of instability following total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Instability following total knee arthroplasty is one of the major causes of revision surgery. In most cases, it can be prevented by using an appropriate prosthesis and a good surgical technique. Particular attention should be given to confirmation of diagnosis for which thorough history taking, complete physical examination and radiographic evaluation are needed. With regard to treatment, identification of the etiology of instability is crucial for establishing proper treatment plans; instability would persist without correction of the cause of the initial instability. For successful revision surgery, balanced medio-lateral and flexion-extension gaps should be achieved. Constrained or rotating-hinge total knee prosthesis should also be considered as an alternative option for certain subsets of patients with instability.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Instability; Knee; Prosthesis failure.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
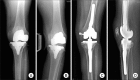

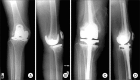
References
-
- Patil SS, Branovacki G, Martin MR, Pulido PA, Levy YD, Colwell CW., Jr 14-year median follow-up using the press-fit condylar sigma design for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1286–1290. - PubMed
-
- Math KR, Zaidi SF, Petchprapa C, Harwin SF. Imaging of total knee arthroplasty. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2006;10:47–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
