Diverse interleukin-7 mRNA transcripts in Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis)
- PMID: 24945249
- PMCID: PMC4063794
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099859
Diverse interleukin-7 mRNA transcripts in Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis)
Abstract
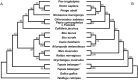
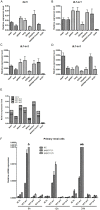
Interleukin-7 (IL7) is a pleiotropic cytokine that is actively involved in the immune system. The Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis) has been proposed as an alternative experimental animal to primates in biomedical research. However, there is a lack of biological knowledge about the immune system of the tree shrew. In this study, we cloned the IL7 gene (tIL7) in the Chinese tree shrew and quantified the expression of mRNA transcripts in eight tissues (heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, intestine, skeletal muscle and brain) from 20 individuals. Eleven tIL7 mRNA transcripts were identified in different tissues. The canonical form (tIL7c) had a length of 1817 bp and encoded a predicted gene product with 177 amino acids. Phylogenetic analyses based on the amino acid sequences revealed a considerably large genetic difference between tree shrew and human. Quantification of mRNA expression of transcripts tIL7c, tIL7-sv1, tIL7-sv2 and tIL7-sv3 showed that these transcripts were expressed in all tissues, albeit the expression levels varied in different tissues. Transcripts tIL7c, tIL7-sv1, and tIL7-sv2 had the lowest expression in brain, and tIL7-sv3 had a dramatically high mRNA expression in skeletal muscle and heart. The mRNA expression levels of tIL7c and tIL7-sv1 were significantly increased upon ploy(I:C) stimulation in tree shrew primary renal cells. As with human full-length IL7, tIL7c, tIL7-sv1, tIL7-sv2 and tIL7-sv3 showed similar a subcellular localization pattern. Our results identified diverse tIL7 transcripts in the Chinese tree shrew, which may play a potential role in modulating IL7-regulated biological effects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

