A large multi-pathogen gastroenteritis outbreak caused by drinking contaminated water from antique neighbourhood fountains, Erzurum city, Turkey, December 2012
- PMID: 24945365
- PMCID: PMC9507095
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268814001459
A large multi-pathogen gastroenteritis outbreak caused by drinking contaminated water from antique neighbourhood fountains, Erzurum city, Turkey, December 2012
Abstract
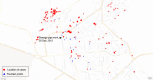
We investigated a gastroenteritis outbreak in Erzurum city, Turkey in December 2012 to identify its cause and mode of transmission. We defined a probable case as onset of diarrhoea (⩾3 episodes/day) or vomiting, plus fever or nausea or abdominal pain during 19-27 December, 2012 in an Erzurum city resident. In a case-control study we compared exposures of 95 randomly selected probable cases and 95 neighbourhood-matched controls. We conducted bacterial culture and real-time multiplex PCR for identification of pathogens. During the week before illness onset, 72% of cases and 15% of controls only drank water from antique neighbourhood fountains; conversely, 16% of cases and 65% of controls only drank bottled or tap water (adjusted odds ratio 20, 95% confidence interval 4·6-84, after controlling for age and sex using conditional logistic regression). Of eight stool specimens collected, two were positive for Shigella sonnei, one for astrovirus, one for astrovirus and norovirus, and one for astrovirus and rotavirus. Water samples from the fountains had elevated total coliform (38-300/100 ml) and Escherichia coli (22-198/100 ml) counts. In conclusion, drinking contaminated fountain water caused this multi-pathogen outbreak. Residents should stop drinking water from these fountains, and clean water from the water treatment plant should be connected to the fountains.
Keywords: waterborne infections.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- UNICEF/WHO. Diarrhoea: why children are still dying and what can be done. New York: United Nations Children's Fund, 2009.
-
- Dick J, Parrish NM. Microbiology tools for the epidemiologist. In: Nelson KE, Williams CM, eds. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Theory and Practice, 2nd edn. Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 2007, pp. 241–277.
-
- Brock TD. Membrane Filtration: A User's Guide and Reference Manual. Madison, WI: Science Tech, 1983.
-
- Gleick PH. The World's Water 2004–2005: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources. Washington, DC: Island Press, 2004.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

