The influence of orthodontic fixed appliances on the oral microbiota: a systematic review
- PMID: 24945514
- PMCID: PMC4296609
- DOI: 10.1590/2176-9451.19.2.046-055.oar
The influence of orthodontic fixed appliances on the oral microbiota: a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether there is scientific evidence to support the hypothesis that the presence of orthodontic fixed appliances influences the oral microbiota.
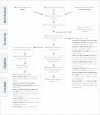
Methods: The search for articles was conducted in PubMed; ISI Web of Knowledge and Ovid databases, including articles published in English until May 17th, 2012. They should report human observational studies presenting the following keywords: "fixed orthodontic appliance" AND "microbiological colonization"; OR "periodontal pathogens"; OR "Streptococcus"; OR "Lactobacillus"; OR "Candida"; OR "Tannerella forsythia"; OR "Treponema denticola"; OR "Fusobacterium nucleatum"; OR "Actimomyces actinomycetemcomitans"; OR "Prevotella intermedia"; OR "Prevotella nigrescens"; OR "Porphyromonas gingivalis". Articles were previously selected by title and abstract. Articles that met the inclusion criteria were analyzed and classified as having low, moderate or high methodology quality. A new detailed checklist for quality assessment was developed based on the information required for applicable data extraction for reviews. The study design, sample, follow-up period, collection and microbial analysis methods, statistical treatment, results and discussion were assessed.
Results: The initial search retrieved 305 articles of which 33 articles were selected by title and abstract. After full-text reading, 8 articles met the inclusion criteria, out of which 4 articles were classified as having low and 4 as moderate methodological quality. The moderate methodological quality studies were included in the systematic review.
Conclusions: The literature revealed moderate evidence that the presence of fixed appliances influences the quantity and quality of oral microbiota.
Objetivo: investigar se há evidências científicas para comprovar a hipótese de que a presença de aparelhos ortodônticos fixos influencia a microbiota bucal.
Métodos: a busca por artigos foi realizada nas bases de dados do PubMed, ISI Web of Knowledge e Ovid, incluindo artigos publicados em inglês até 17 de maio de 2012. Esses deveriam relatar estudos observacionais humanos que apresentassem as palavras-chave: "aparelho ortodôntico fixo" e "colonização microbiológica"; ou "patógenos periodontais"; ou "Streptococcus"; ou "Lactobacillus"; ou "Candida"; ou "Tannerella forsythia"; ou "Treponema denticola"; ou "Fusobacterium nucleatum"; ou "Actimomyces actinomycetemcomitans"; ou "Prevotella intermedia"; ou "Prevotella nigrescens"; ou "Porphyromonas gingivalis". Artigos foram previamente selecionados pelo título e resumo. Artigos que atenderam aos critérios de inclusão foram analisados e classificados como de baixa, moderada ou alta qualidade metodológica. Uma nova lista de verificação detalhada para avaliação da qualidade foi desenvolvida, com base na informação necessária para a extração de dados aplicáveis para as revisões de literatura. O desenho do estudo, a amostra, o período de acompanhamento, coleta e métodos de análise microbiana, o tratamento estatístico, resultados e discussão foram avaliados.
Resultados: a busca inicial encontrou 305 trabalhos. Em seguida, 33 artigos foram selecionados pelo título e resumo. Após a leitura do texto completo, apenas oito artigos preencheram os critérios de inclusão. Desses, quatro foram classificados como artigos com baixa qualidade metodológica e quatro como moderados. Os estudos de qualidade metodológica moderada foram incluídos na revisão sistemática.
Conclusão: a literatura revelou evidência moderada de que a presença de aparelhos fixos exerce influência na quantidade e qualidade da microbiota bucal.
Keywords: Attachment sites; Microbiological analysis; Microbiology; Orthodontic appliances; Periodontics.
Figures
References
-
- Campbel CHCT. Alterações da microflora bucal em pacientes portadores de aparelho ortodôntico fixo [tese] Rio de Janeiro (RJ): Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro; 2001.
-
- Balenseifen JW, Madonia JV. Study of dental plaque in orthodontic patients. J Dent Res. 1970;49(2):320–324. - PubMed
-
- Chin MYH, Busscher HJ, Evans R, Noar J, Pratten E. Early biofilm formation and the effects of antimicrobial agents on orthodontics bonding materials in a parallel plate flow chamber. Eur J Orthod. 2006;28(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Friedman M, Harari D, Raz H, Golomb G, Brayer L. Plaque Inhibition by sustained of Chlorhexidine from removable appliances. J Dent Res. 1985;64(11):1319–1321. - PubMed
-
- Hagg U, Kaveewatcharanont P, Samaranayake YH, Samaranayake LP. The effect of fixed orthodontic appliances on the oral carriage of candida species and enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Orthod. 2004;26(6):623–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous