Identification of late larval stage developmental checkpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans regulated by insulin/IGF and steroid hormone signaling pathways
- PMID: 24945623
- PMCID: PMC4063711
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004426
Identification of late larval stage developmental checkpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans regulated by insulin/IGF and steroid hormone signaling pathways
Abstract
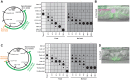
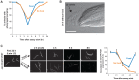
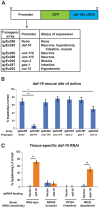
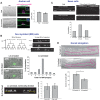
Organisms in the wild develop with varying food availability. During periods of nutritional scarcity, development may slow or arrest until conditions improve. The ability to modulate developmental programs in response to poor nutritional conditions requires a means of sensing the changing nutritional environment and limiting tissue growth. The mechanisms by which organisms accomplish this adaptation are not well understood. We sought to study this question by examining the effects of nutrient deprivation on Caenorhabditis elegans development during the late larval stages, L3 and L4, a period of extensive tissue growth and morphogenesis. By removing animals from food at different times, we show here that specific checkpoints exist in the early L3 and early L4 stages that systemically arrest the development of diverse tissues and cellular processes. These checkpoints occur once in each larval stage after molting and prior to initiation of the subsequent molting cycle. DAF-2, the insulin/insulin-like growth factor receptor, regulates passage through the L3 and L4 checkpoints in response to nutrition. The FOXO transcription factor DAF-16, a major target of insulin-like signaling, functions cell-nonautonomously in the hypodermis (skin) to arrest developmental upon nutrient removal. The effects of DAF-16 on progression through the L3 and L4 stages are mediated by DAF-9, a cytochrome P450 ortholog involved in the production of C. elegans steroid hormones. Our results identify a novel mode of C. elegans growth in which development progresses from one checkpoint to the next. At each checkpoint, nutritional conditions determine whether animals remain arrested or continue development to the next checkpoint.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- McCue MD (2010) Starvation physiology: reviewing the different strategies animals use to survive a common challenge. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 156: 1–18. - PubMed
-
- Golden JW, Riddle DL (1984) The Caenorhabditis elegans dauer larva: developmental effects of pheromone, food, and temperature. Dev Biol 102: 368–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

