Evaluation of anticonvulsant actions of dibromophenyl enaminones using in vitro and in vivo seizure models
- PMID: 24945912
- PMCID: PMC4063795
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099770
Evaluation of anticonvulsant actions of dibromophenyl enaminones using in vitro and in vivo seizure models
Abstract
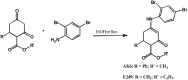
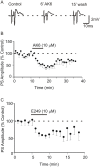
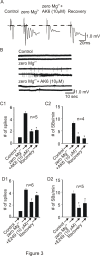
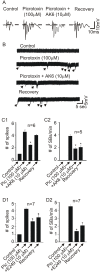
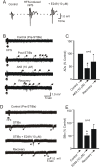
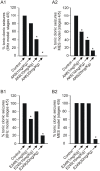
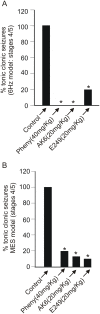
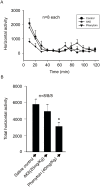
Epilepsy and other seizure disorders are not adequately managed with currently available drugs. We recently synthesized a series of dibromophenyl enaminones and demonstrated that AK6 and E249 were equipotent to previous analogs but more efficacious in suppressing neuronal excitation. Here we examined the actions of these lead compounds on in vitro and in vivo seizure models. In vitro seizures were induced in the hippocampal slice chemically (zero Mg2+ buffer and picrotoxin) and electrically using patterned high frequency stimulation (HFS) of afferents. In vivo seizures were induced in rats using the 6 Hz and the maximal electroshock models. AK6 (10 µM) and E249 (10 µM) depressed the amplitude of population spikes recorded in area CA1 of the hippocampus by -50.5±4.3% and -40.1±3.1% respectively, with partial recovery after washout. In the zero Mg2+ model, AK6 (10 µM) depressed multiple population spiking (mPS) by -59.3±6.9% and spontaneous bursts (SBs) by -65.9±7.2% and in the picrotoxin-model by -43.3±7.2% and -50.0±8.3%, respectively. Likewise, E249 (10 µM) depressed the zero-Mg2+-induced mPS by -48.8±9.5% and SBs by -55.8±15.5%, and in the picrotoxin model by -37.1±5.5% and -56.5±11.4%, respectively. They both suppressed post-HFS induced afterdischarges and SBs. AK6 and E249 dose-dependently protected rats in maximal electroshock and 6 Hz models of in vivo seizures after 30 min pretreatment. Their level of protection in both models was similar to that obtained with phenytoin Finally, while AK6 had no effect on locomotion in rats, phenytoin significantly decreased locomotion. AK6 and E249, suppressed in vitro and in vivo seizures to a similar extent. Their in vivo activities are comparable with but not superior to phenytoin. The most efficacious, AK6 produced no locomotor suppression while phenytoin did. Thus, AK6 and E249 may be excellent candidates for further investigation as potential agents for the treatment of epilepsy syndromes with possibly less CNS side effects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel actions of oxazolidinones: in vitro screening of a triazolyloxazolidinone for anticonvulsant activity.Med Princ Pract. 2013;22(4):340-5. doi: 10.1159/000346005. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Med Princ Pract. 2013. PMID: 23257573 Free PMC article.
-
Anticonvulsant enaminone E139 suppresses epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal slices.Epilepsy Res. 2007 Sep;76(2-3):85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.07.001. Epub 2007 Aug 28. Epilepsy Res. 2007. PMID: 17728105
-
Rosiglitazone Suppresses In Vitro Seizures in Hippocampal Slice by Inhibiting Presynaptic Glutamate Release in a Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0144806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144806. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26659605 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y suppresses epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus in vitro.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Sep;78(3):1651-61. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.3.1651. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9310450
-
Design, synthesis and anticonvulsant evaluation of fluorinated benzyl amino enaminones.Bioorg Med Chem. 2019 Jan 1;27(1):161-166. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.11.033. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30503782
Cited by
-
Hippocampal Disinhibition Reduces Contextual and Elemental Fear Conditioning While Sparing the Acquisition of Latent Inhibition.eNeuro. 2022 Jan 21;9(1):ENEURO.0270-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0270-21.2021. Print 2022 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 34980662 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the antinociceptive activities of enaminone compounds on the formalin and hot plate tests in mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 26;6:21582. doi: 10.1038/srep21582. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26916642 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone Potentiates the Effect of Phenytoin against Electroshock-Induced Convulsions in Rats by Reducing the Hyperactivation of m-TOR Pathway and Neuroinflammation: Evidence from In Vivo, In Vitro and Computational Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 8;14(11):1132. doi: 10.3390/ph14111132. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delgado-Escueta AV, Wilson WA, Olsen RW, Porter RJ (1999) New waves of research in the epilepsies: crossing into the third millennium. Adv Neurol 79: 3–58. - PubMed
-
- McCormick DA, Contreras D (2001) On the cellular and network bases of epileptic seizures. Annu Rev Physiol 63: 815–846. - PubMed
-
- Loscher W, Schmidt D (2002) New horizons in the development of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Res 50: 3–16. - PubMed
-
- Pollard JR, French J (2006) Antiepileptic drugs in development. Lancet Neurol 5: 1064–1067. - PubMed
-
- Santhouse J, Carrier C, Arya S, Fowler H, Duncan S (2007) A Comparison of Self-reported Quality of Life between Patients with Epilepsy and Neurocardiogenic Syncope. Epilepsia. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

