Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in mice
- PMID: 24946165
- PMCID: PMC4253455
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12823
Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: IL-31, which is described as a pruritogenic cytokine, is linked to the itching that is associated with allergic and non-allergic eczema, but the precise pruritogenic mechanism of IL-31 and its potential as a therapeutic target for atopic dermatitis (AD) have not been determined.
Experimental approach: We investigated the effects of existing drugs on the scratching behaviour induced by an i.v. injection of IL-31 to clarify whether IL-31 induced pruritus indirectly. In addition, we studied the effects of an anti-IL-31 receptor α subunit (anti-IL-31 receptor α) neutralizing antibody on chronic pruritus-inducing dermatitis in an AD-like model to determine whether IL-31 not only induces scratching behaviour, but is also the causative factor in an AD phenotype.
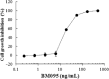
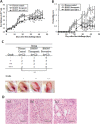
Key results: The scratching behaviour induced by an i.v. injection of IL-31 was inhibited by pretreatment with an anti-IL-31 receptor α-neutralizing antibody. In contrast, it was not inhibited significantly by a non-sedative antihistamine (terfenadine), immunosuppressants (dexamethasone and tacrolimus), or a μ-opioid receptor antagonist (naloxone). The anti-IL-31 receptor α-neutralizing antibody reduced the ear swelling and dermatitis score in a chronic pruritus-inducing AD-like model. Moreover, treatment with the anti-IL-31 receptor α-neutralizing antibody showed therapeutic effects on the dermatitis even if it was injected after the disease had developed.
Conclusions and implications: Anti-IL-31 receptor α is a potential novel therapeutic approach for escaping from the itch-scratch cycle and also a treatment for dermatitis in AD.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Arai I, Tsuji M, Takeda H, Akiyama N, Saito S. A single dose of interleukin-31 (IL-31) causes continuous itch-associated scratching behaviour in mice. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:669–671. - PubMed
-
- Assmann T, Homey B, Ruzicka T. Topical tacrolimus for the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2001;2:1167–1175. - PubMed
-
- Bando T, Morikawa Y, Komori T, Senba E. Complete overlap of interleukin-31 receptor A and oncostatin M receptor beta in the adult dorsal root ganglia with distinct developmental expression patterns. Neuroscience. 2006;142:1263–1271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

