Functional interplay between ATM/ATR-mediated DNA damage response and DNA repair pathways in oxidative stress
- PMID: 24947324
- PMCID: PMC4176976
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1666-4
Functional interplay between ATM/ATR-mediated DNA damage response and DNA repair pathways in oxidative stress
Abstract
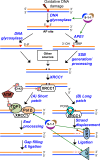
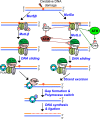
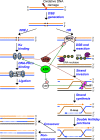
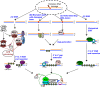
To maintain genome stability, cells have evolved various DNA repair pathways to deal with oxidative DNA damage. DNA damage response (DDR) pathways, including ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 checkpoints, are also activated in oxidative stress to coordinate DNA repair, cell cycle progression, transcription, apoptosis, and senescence. Several studies demonstrate that DDR pathways can regulate DNA repair pathways. On the other hand, accumulating evidence suggests that DNA repair pathways may modulate DDR pathway activation as well. In this review, we summarize our current understanding of how various DNA repair and DDR pathways are activated in response to oxidative DNA damage primarily from studies in eukaryotes. In particular, we analyze the functional interplay between DNA repair and DDR pathways in oxidative stress. A better understanding of cellular response to oxidative stress may provide novel avenues of treating human diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Sies H. Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol. 1997;82(2):291–295. - PubMed
-
- Betteridge DJ. What is oxidative stress? Metabolism. 2000;49(2 Suppl 1):3–8. - PubMed
-
- Jones DP. Redefining oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8(9–10):1865–1879. - PubMed
-
- Agnez-Lima LF, Melo JT, Silva AE, Oliveira AH, Timoteo AR, Lima-Bessa KM, Martinez GR, Medeiros MH, Di Mascio P, Galhardo RS, Menck CF. DNA damage by singlet oxygen and cellular protective mechanisms. Mutat Res. 2012;751(1):15–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

