Changes in glucose and fat metabolism in response to the administration of a hepato-preferential insulin analog
- PMID: 24947349
- PMCID: PMC4392933
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-0266
Changes in glucose and fat metabolism in response to the administration of a hepato-preferential insulin analog
Abstract
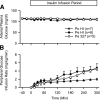
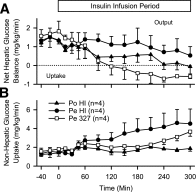
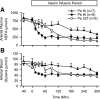
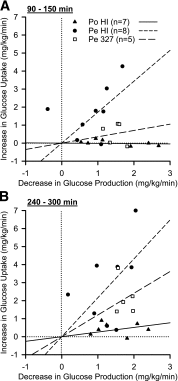
Endogenous insulin secretion exposes the liver to three times higher insulin concentrations than the rest of the body. Because subcutaneous insulin delivery eliminates this gradient and is associated with metabolic abnormalities, functionally restoring the physiologic gradient may provide therapeutic benefits. The effects of recombinant human insulin (HI) delivered intraportally or peripherally were compared with an acylated insulin model compound (insulin-327) in dogs. During somatostatin and basal portal vein glucagon infusion, insulin was infused portally (PoHI; 1.8 pmol/kg/min; n = 7) or peripherally (PeHI; 1.8 pmol/kg/min; n = 8) and insulin-327 (Pe327; 7.2 pmol/kg/min; n = 5) was infused peripherally. Euglycemia was maintained by glucose infusion. While the effects on liver glucose metabolism were greatest in the PoHI and Pe327 groups, nonhepatic glucose uptake increased most in the PeHI group. Suppression of lipolysis was greater during PeHI than PoHI and was delayed in Pe327 infusion. Thus small increments in portal vein insulin have major consequences on the liver, with little effect on nonhepatic glucose metabolism, whereas insulin delivered peripherally cannot act on the liver without also affecting nonhepatic tissues. Pe327 functionally restored the physiologic portal-arterial gradient and thereby produced hepato-preferential effects.
© 2014 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures


References
-
- Greco AV, Crucitti F, Ghirlanda G, et al. Insulin and glucagon concentrations in portal and peripheral veins in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Diabetologia 1979;17:23–28 - PubMed
-
- Song SH, McIntyre SS, Shah H, Veldhuis JD, Hayes PC, Butler PC. Direct measurement of pulsatile insulin secretion from the portal vein in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:4491–4499 - PubMed
-
- Sindelar DK, Balcom JH, Chu CA, Neal DW, Cherrington AD. A comparison of the effects of selective increases in peripheral or portal insulin on hepatic glucose production in the conscious dog. Diabetes 1996;45:1594–1604 - PubMed
-
- Sindelar DK, Chu CA, Neal DW, Cherrington AD. Interaction of equal increments in arterial and portal vein insulin on hepatic glucose production in the dog. Am J Physiol 1997;273:E972–E980 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

