Mechanisms of increased in vivo insulin sensitivity by dietary methionine restriction in mice
- PMID: 24947368
- PMCID: PMC4207389
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-0464
Mechanisms of increased in vivo insulin sensitivity by dietary methionine restriction in mice
Abstract
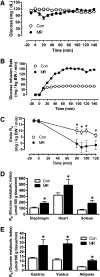
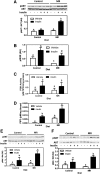
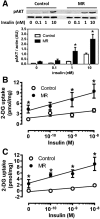
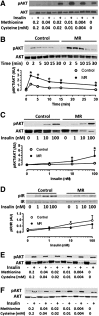
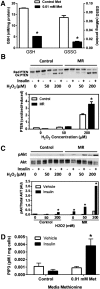
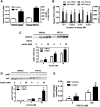
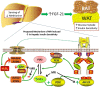
To understand the physiological significance of the reduction in fasting insulin produced by dietary methionine restriction (MR), hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps were used to examine the effect of the diet on overall and tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in mice. The steady-state glucose infusion rate was threefold higher in the MR group and consistent with the 2.5- to threefold increase in 2-deoxyglucose uptake in skeletal muscle, heart, and white adipose tissue. Dietary MR enhanced suppression of hepatic glucose production by insulin, enhanced insulin-dependent Akt phosphorylation in the liver, and increased hepatic expression and circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) by fourfold. Limitation of media methionine recapitulated amplification of Akt phosphorylation by insulin in HepG2 cells but not in 3T3-L1 adipocytes or C2C12 myotubes. Amplification of insulin signaling in HepG2 cells by MR was associated with reduced glutathione, where it functions as a cofactor for phosphatase and tensin homolog. In contrast, FGF-21, but not restricting media methionine, enhanced insulin-dependent Akt phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. These findings provide a potential mechanism for the diet-induced increase in insulin sensitivity among tissues that involves a direct effect of methionine in liver and an indirect effect in adipose tissue through MR-dependent increases in hepatic transcription and release of FGF-21.
© 2014 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures
References
-
- Orentreich N, Matias JR, DeFelice A, Zimmerman JA. Low methionine ingestion by rats extends life span. J Nutr 1993;123:269–274 - PubMed
-
- Richie JP, Jr, Leutzinger Y, Parthasarathy S, Malloy V, Orentreich N, Zimmerman JA. Methionine restriction increases blood glutathione and longevity in F344 rats. FASEB J 1994;8:1302–1307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NIH DK-059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK098918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021945/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096311/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32-DK-098918-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20-GM-103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK-096311/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM118430/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

