Direct measurements of SR free Ca reveal the mechanism underlying the transient effects of RyR potentiation under physiological conditions
- PMID: 24947416
- PMCID: PMC4145011
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvu158
Direct measurements of SR free Ca reveal the mechanism underlying the transient effects of RyR potentiation under physiological conditions
Abstract
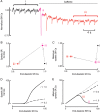
Aims: Most of the calcium that activates contraction is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) through the ryanodine receptor (RyR). It is controversial whether activators of the RyR produce a maintained increase in the amplitude of the systolic Ca transient. We therefore aimed to examine the effects of activation of the RyR in large animals under conditions designed to be as physiological as possible while simultaneously measuring SR and cytoplasmic Ca.
Methods and results: Experiments were performed on ventricular myocytes from canine and ovine hearts. Cytoplasmic Ca was measured with fluo-3 and SR Ca with mag-fura-2. Application of caffeine resulted in a brief increase in the amplitude of the systolic Ca transient accompanied by an increase of action potential duration. These effects disappeared with a rate constant of ∼3 s(-1). Similar effects were seen in cells taken from sheep in which heart failure had been induced by rapid pacing. The decrease of Ca transient amplitude was accompanied by a decrease of SR Ca content. During this phase, the maximum (end-diastolic) SR Ca content fell while the minimum systolic increased.
Conclusions: This study shows that, under conditions designed to be as physiological as possible, potentiation of RyR opening has no maintained effect on the systolic Ca transient. This result makes it unlikely that potentiation of the RyR has a maintained role in positive inotropy.
Keywords: Calcium; Ryanodine receptor; Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

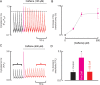

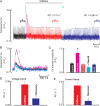
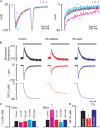
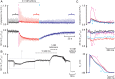
References
-
- Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 2002;415:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Meissner G. Regulation of mammalian ryanodine receptors. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d2072–d2080. - PubMed
-
- Terentyev D, Gyorke I, Belevych AE, Terentyeva R, Sridhar A, Nishijima Y, de Blanco EC, Khanna S, Sen CK, Cardounel AJ, Carnes CA, Gyorke S. Redox modification of ryanodine receptors contributes to sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak in chronic heart failure. Circ Res. 2008;103:1466–1472. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zima AV, Blatter LA. Redox regulation of cardiac calcium channels and transporters. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;71:310–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FS/10/71/28563/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/10/89/28630/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/08/078/25593/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/12/57/29717/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/09/036/27823/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

