Comparative intrauterine development and placental function of ART concepti: implications for human reproductive medicine and animal breeding
- PMID: 24947475
- PMCID: PMC4196686
- DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmu032
Comparative intrauterine development and placental function of ART concepti: implications for human reproductive medicine and animal breeding
Abstract
Background: The number of children conceived using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) has reached >5 million worldwide and continues to increase. Although the great majority of ART children are healthy, many reports suggest a forthcoming risk of metabolic complications, which is further supported by the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease hypothesis of suboptimal embryo/fetal conditions predisposing adult cardiometabolic pathologies. Accumulating evidence suggests that fetal and placental growth kinetics are important features predicting post-natal health, but the relationship between ART and intrauterine growth has not been systematically reviewed.
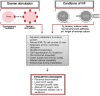
Methods: Relevant studies describing fetoplacental intrauterine phenotypes of concepti generated by in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) in the mouse, bovine and human were comprehensively researched using PubMed and Google Scholar. Intrauterine growth plots were created from tabular formatted data available in selected reports.
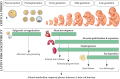
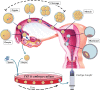
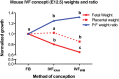
Results: ART pregnancies display minor but noticeable alterations in fetal and placental growth curves across mammalian species. In all species, there is evidence of fetal growth restriction in the earlier stages of pregnancy, followed by significant increases in placental size and accelerated fetal growth toward the end of gestation. However, there is a species-specific effect of ART on birthweights, that additionally vary in a culture condition-, strain-, and/or stage at transfer-specific manner. We discuss the potential mechanisms that underlie these changes, and how they are affected by specific components of ART procedures.
Conclusions: ART may promote measurable alterations to intrauterine growth trajectory and placental function. Key findings include evidence that birthweight is not a reliable marker of fetal stress, and that increases in embryo manipulation result in more deviant fetal growth curves. Because growth kinetics in early life are particularly relevant to adult metabolic physiology, we advise more rigorous assessment of fetal growth and placental function in human ART pregnancies, as well as continued follow-up of ART offspring throughout post-natal life. Finally, strategies to minimize embryo manipulations should be adopted whenever possible.
Keywords: Developmental Origins of Health and Disease; IVF; assisted reproductive technology; fetal and placental growth.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Adjaye J, Huntriss J, Herwig R, BenKahla A, Brink TC, Wierling C, Hultschig C, Groth D, Yaspo ML, Picton HM, et al. Primary differentiation in the human blastocyst: comparative molecular portraits of inner cell mass and trophectoderm cells. Stem Cells. 2005;23:1514–1525. - PubMed
-
- Audette MC, Greenwood SL, Sibley CP, Jones CJ, Challis JR, Matthews SG, Jones RL. Dexamethasone stimulates placental system A transport and trophoblast differentiation in term villous explants. Placenta. 2010;31:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Audette MC, Challis JR, Jones RL, Sibley CP, Matthews SG. Antenatal dexamethasone treatment in midgestation reduces system A-mediated transport in the late-gestation murine placenta. Endocrinology. 2011;152:3561–3570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

