The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: a new perspective
- PMID: 24948110
- PMCID: PMC4221543
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28864
The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: a new perspective
Abstract
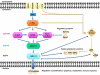
The mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated (MAPK/ERK) pathway is activated by upstream genomic events and/or activation of multiple signaling events in which information coalesces at this important nodal pathway point. This pathway is tightly regulated under normal conditions by phosphatases and bidirectional communication with other pathways, like the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (AKT/m-TOR) pathway. Recent evidence indicates that the MAPK/ERK signaling node can function as a tumor suppressor as well as the more common pro-oncogenic signal. The effect that predominates depends on the intensity of the signal and the context or tissue in which the signal is aberrantly activated. Genomic profiling of tumors has revealed common mutations in MAPK/ERK pathway components, such as v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF). Currently approved for the treatment of melanoma, inhibitors of BRAF kinase are being studied alone and in combination with inhibitors of the MAPK and other pathways to optimize the treatment of many tumor types. Therapies targeted toward MAPK/ERK components have various response rates when used in different solid tumors, such as colorectal cancer and ovarian cancer. Understanding the differential nature of activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway in each tumor type is critical in developing single and combination regimens, because different tumors have unique mechanisms of primary and secondary signaling and subsequent sensitivity to drugs.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); melanoma; mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase (MEK); ovarian cancer; signaling; v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (BRAF).
© 2014 American Cancer Society.
Figures

References
-
- Weinstein IB, Joe A. Oncogene addiction. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9):3077–80. discussion 80. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74. - PubMed
-
- De Luca A, Maiello MR, D’Alessio A, Pergameno M, Normanno N. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16(Suppl 2):S17–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

