Neuronal ensembles in amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex track differential components of contextual fear
- PMID: 24948801
- PMCID: PMC4061389
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3624-13.2014
Neuronal ensembles in amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex track differential components of contextual fear
Abstract
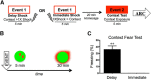
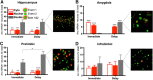
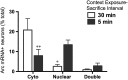
Although the circuit mediating contextual fear conditioning has been extensively described, the precise contribution that specific anatomical nodes make to behavior has not been fully elucidated. To clarify the roles of the dorsal hippocampus (DH), basolateral amygdala (BLA), and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in contextual fear conditioning, activity within these regions was mapped using cellular compartment analysis of temporal activity using fluorescence in situ hybridization (catFISH) for Arc mRNA. Rats were delay-fear conditioned or immediately shocked (controls) and thereafter reexposed to the shocked context to test for fear memory recall. Subsequent catFISH analyses revealed that in the DH, cells were preferentially reactivated during the context test, regardless of whether animals had been fear conditioned or immediately shocked, suggesting that the DH encodes spatial information specifically, rather then the emotional valence of an environment. In direct contrast, neuronal ensembles in the BLA were only reactivated at test if animals had been fear conditioned, suggesting that the amygdala specifically tracks the emotional properties of a context. Interestingly, Arc expression in the mPFC was consistent with both amygdala- and hippocampus-like patterns, supporting a role for the mPFC in both fear and contextual processing. Collectively, these data provide crucial insight into the region-specific behavior of neuronal ensembles during contextual fear conditioning and demonstrate a dissociable role for the hippocampus and amygdala in processing the contextual and emotional properties of a fear memory.
Keywords: Arc; amygdala; catFISH; contextual fear; hippocampus; prefrontal cortex.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/348462-05$15.00/0.
Figures
References
-
- Chawla MK, Guzowski JF, Ramirez-Amaya V, Lipa P, Hoffman KL, Marriott LK, Worley PF, McNaughton BL, Barnes CA. Sparse, environmentally selective expression of Arc RNA in the upper blade of the rodent fascia dentata by brief spatial experience. Hippocampus. 2005;15:579–586. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20091. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fanselow MS. Factors governing one-trial contextual conditioning. Anim Learn Behav. 1990;18:264–270. doi: 10.3758/BF03205285. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
