Nrf2 upregulates ATP binding cassette transporter expression and activity at the blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers
- PMID: 24948812
- PMCID: PMC4061395
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2935-13.2014
Nrf2 upregulates ATP binding cassette transporter expression and activity at the blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers
Abstract
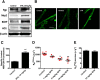
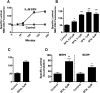
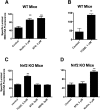
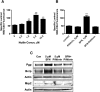
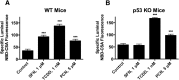
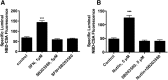
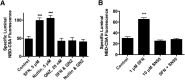
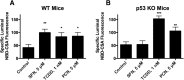
Activation of nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2), a sensor of oxidative stress, is neuroprotective in animal models of cerebral ischemia, traumatic brain injury, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and spinal cord injury. We show here that Nrf2 activation with sulforaphane (SFN) in vivo or in vitro increases expression and transport activity of three ATP-driven drug efflux pumps at the blood-brain barrier [P-glycoprotein, ATP binding cassette b1 (Abcb1); multidrug resistance-associated protein-2 (Mrp2), Abcc2; and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp), Abcg2]. Dosing rats with SFN increased protein expression of all three transporters in brain capillaries and decreased by 50% brain accumulation of the P-glycoprotein substrate verapamil. Exposing rat or mouse brain capillaries to SFN increased P-glycoprotein, Bcrp, and Mrp2 transport activity and protein expression; SFN increased P-glycoprotein activity in mouse spinal cord capillaries. Inhibiting transcription or translation abolished upregulation of P-glycoprotein activity. No such effects were seen in brain capillaries from Nrf2-null mice, indicating Nrf2 dependence. Nrf2 signaled indirectly to increase transporter activity/expression. The p53 inhibitor pifithrin abolished the SFN-induced increase in transporter activity/expression, and the p53-activator nutlin-3 increased P-glycoprotein activity. SFN did not alter P-glycoprotein transport activity in brain and spinal cord capillaries from p53-null mice. Inhibitors of p38 MAPK and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) blocked the effects of SFN and nutlin-3 on P-glycoprotein activity. These results implicate Nrf2, p53, and NF-κB in the upregulation of P-glycoprotein, Bcrp, and Mrp2 at blood-CNS barriers. They imply that the barriers are tightened selectively (efflux transporter upregulation) by oxidative stress, providing increased neuroprotection, but also reduced penetration of many therapeutic drugs.
Keywords: ABC transporters; NF-κB; P-glycoprotein; blood-brain barrier; drug delivery; p53.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/348585-09$15.00/0.
Figures

References
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Fricker G, Miller DS. Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:413–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
