Characterization of newly isolated oleaginous yeasts - Cryptococcus podzolicus, Trichosporon porosum and Pichia segobiensis
- PMID: 24949259
- PMCID: PMC4052688
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-014-0024-0
Characterization of newly isolated oleaginous yeasts - Cryptococcus podzolicus, Trichosporon porosum and Pichia segobiensis
Abstract
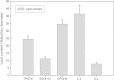
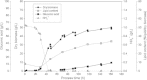
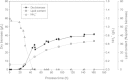
The yeast strains Cryptococcus podzolicus, Trichosporon porosum and Pichia segobiensis were isolated from soil samples and identified as oleaginous yeast strains beneficial for the establishment of microbial production processes for sustainable lipid production suitable for several industrial applications. When cultured in bioreactors with glucose as the sole carbon source C. podzolicus yielded 31.8% lipid per dry biomass at 20°C, while T. porosum yielded 34.1% at 25°C and P. segobiensis 24.6% at 25°C. These amounts correspond to lipid concentrations of 17.97 g/L, 17.02 g/L and 12.7 g/L and volumetric productivities of 0.09 g/Lh, 0.1 g/Lh and 0.07 g/Lh, respectively. During the culture of C. podzolicus 30 g/l gluconic acid was detected as by-product in the culture broth and 12 g/L gluconic acid in T. porosum culture. The production of gluconic acid was eliminated for both strains when glucose was substituted by xylose as the carbon source. Using xylose lipid yields were 11.1 g/L and 13.9 g/L, corresponding to 26.8% and 33.4% lipid per dry biomass and a volumetric productivity of 0.07 g/Lh and 0.09 g/Lh, for C. podzolicus and T. porosum respectively. The fatty acid profile analysis showed that oleic acid was the main component (39.6 to 59.4%) in all three strains and could be applicable for biodiesel production. Palmitic acid (18.4 to 21.1%) and linolenic acid (7.5 to 18.7%) are valuable for cosmetic applications. P. segobiensis had a considerable amount of palmitoleic acid (16% content) and may be suitable for medical applications.
Keywords: Cryptococcus podzolicus; Microbial lipid production; Oleaginous yeasts; Pichia segobiensis; Screening; Trichosporon porosum.
Figures



References
-
- Al-mhanna MNM. Observation of Crabtree effect and diauxic behaviour of yeast by using absorption. Chem Eng Trans. 2010;4:1465–1470. doi:10.3303/CET1021245.
-
- Botes AL, Lotter J, Rhode OHJ, Botha A. Interspecies differences in the enantioselectivity of epoxide hydrolases in Cryptococcus laurentii (Kufferath) C.E. skinner and Cryptococcus podzolicus (Bab’jeva & Reshetova) Golubev. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2005;4(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2004.10.003. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2004.10.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Evans CT, Ratledge C, Gilbert SC. A rapid screening method for lipid accumulating yeast using a replica printing technique. J Microbiol Methods. 1985;4(3–4):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0167-7012(85)90038-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

