Impact of a surgical intensivist on the clinical outcomes of patients admitted to a surgical intensive care unit
- PMID: 24949324
- PMCID: PMC4062451
- DOI: 10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.319
Impact of a surgical intensivist on the clinical outcomes of patients admitted to a surgical intensive care unit
Abstract
Purpose: An intensivist is a key factor in the mortality of patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of an intensivist on clinical outcomes of patients admitted to a surgical ICU.
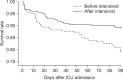
Methods: During the study period, the surgical ICU was converted from an open ICU to an intensivist-directed ICU managed by an intensivist who was board certified in both general surgery and critical care medicine. We compared consecutive patients admitted to the surgical ICU before and after implementing the intensivist-directed care. The primary outcome was ICU mortality, and secondary outcomes were hospital mortality, 90-day mortality, length of hospital stay, ICU-free days, ventilator-free days, and ICU readmission rate.
Results: A total of 441 patients were included in this study: 188 before implementation of the intensivist and 253 after implementation. Clinical characteristics were not different between the two groups. ICU mortality decreased from 11.7% to 6.3% (P = 0.047) after implementation, and 90-day mortality also decreased significantly (P = 0.008). The adjusted hazard ratio of the intensivist for ICU mortality was 0.43 (95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.87; P = 0.020). ICU-free days (P = 0.013) and the hospital length of stay (P = 0.032) were significantly improved after implementing the intensivist-directed care. Before implementation period, 16.0% of patients were readmitted, compared with only 9.9% after implementation (P = 0.05).
Conclusion: Implementing intensivist-directed care in the surgical ICU was associated with significant improvements in ICU mortality and significant clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Critical illness; General surgery; Intensive care units; Mortality; Specialization.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implementation of a Surgical Intensivist Model Increases Palliative Care Consultation in the Care of Trauma ICU Patients.Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2022 Mar;39(3):270-273. doi: 10.1177/10499091211025733. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2022. PMID: 34235976
-
Admission to surgical intensive care unit in time with intensivist coverage and its association with postoperative 30-day mortality: The role of intensivists in a surgical intensive care unit.Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2019 Jun;38(3):259-263. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2019. PMID: 30342104
-
The Impact of Implementing an Intensivist Model With Nighttime In-Hospital Nocturnist and Effect on ICU Outcomes.J Intensive Care Med. 2020 May;35(5):461-467. doi: 10.1177/0885066618758246. Epub 2018 Feb 19. J Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 29458294
-
Potential reduction in mortality rates using an intensivist model to manage intensive care units.Eff Clin Pract. 2000 Nov-Dec;3(6):284-9. Eff Clin Pract. 2000. PMID: 11151525 Review.
-
Quality Indicators in Adult Critical Care Medicine.Glob J Qual Saf Healthc. 2024 May 2;7(2):75-84. doi: 10.36401/JQSH-23-30. eCollection 2024 May. Glob J Qual Saf Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38725886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical impact of physician staffing transition in intensive care units: a retrospective observational study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Nov 26;22(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01905-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 36435755 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges experienced by health care professionals working in resource-poor intensive care settings in the Limpopo province of South Africa.Curationis. 2019 Mar 26;42(1):e1-e8. doi: 10.4102/curationis.v42i1.1921. Curationis. 2019. PMID: 31038326 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the clinical impact of cardiac intensivists in cardiac intensivecare units: results from the RESCUE registry.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Feb 21;25(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04559-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 39984837 Free PMC article.
-
Selecting the right patients is the key.Afr J Thorac Crit Care Med. 2018 Apr 3;24(1):10.7196/AJTCCM2018.v24i1.204. doi: 10.7196/AJTCCM2018.v24i1.204. eCollection 2018. Afr J Thorac Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 34541490 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Impact of Improved Oral Care Methods on the Oral Health of Patients Undergoing Transoral Mechanical Ventilation.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Sep 16;2022:7596654. doi: 10.1155/2022/7596654. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9823261. doi: 10.1155/2023/9823261. PMID: 36158118 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Pronovost P, Thompson DA, Holzmueller CG, Dorman T, Morlock LL. Impact of the Leapfrog Group's intensive care unit physician staffing standard. J Crit Care. 2007;22:89–96. - PubMed
-
- Pronovost PJ, Angus DC, Dorman T, Robinson KA, Dremsizov TT, Young TL. Physician staffing patterns and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: a systematic review. JAMA. 2002;288:2151–2162. - PubMed
-
- Carson SS, Stocking C, Podsadecki T, Christenson J, Pohlman A, MacRae S, et al. Effects of organizational change in the medical intensive care unit of a teaching hospital: a comparison of 'open' and 'closed' formats. JAMA. 1996;276:322–328. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources