Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration: from the past to the future
- PMID: 24949369
- PMCID: PMC4062239
- DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.117691
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration: from the past to the future
Abstract
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) is a technique which allows the study of cells obtained through aspiration in different locations near the gastrointestinal tract. EUS-FNA is used to acquire tissue from mucosal/submucosal tumors, as well as peri-intestinal structures including lymph nodes, pancreas, adrenal gland, gallbladder, bile duct, liver, kidney, lung, etc. The pancreas and lymph nodes are still the most common organs targeted in EUS-FNA. The overall accuracy of EUS is superior to computed tomography scan and magnetic resonance imaging for detecting pancreatic lesions. In most cases it is possible to avoid unnecessary surgical interventions in advanced pancreatic cancer, and EUS is considered the preferred method for loco-regional staging of pancreatic cancer. FNA improved the sensitivity and specificity compared to EUS imaging alone in detection of malignant lymph nodes. The negative predictive value of EUS-FNA is relatively low. The presence of a cytopathologist during EUS-FNA improves the diagnostic yield, decreasing unsatisfactory samples or need for additional passes, and consequently the procedural time. The size of the needle is another factor that could modify the diagnostic accuracy of EUS-FNA. Even though the EUS-FNA technique started in early nineteen's, there are many remarkable progresses culminating nowadays with the discovery and performance of needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Last, but not least, identification and quantification of potential molecular markers for pancreatic cancer on cellular samples obtained by EUS-FNA could be a promising approach for the diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses.
Keywords: confocal laser endomicroscopy; endoscopic ultrasound; fine needle aspiration.
Figures


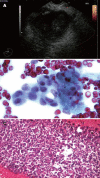

References
-
- Diamantis A, Magiorkinis E, Koutselini H. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: historical aspects. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2009;47:191–7. - PubMed
-
- Logroño R, Waxman I. Interactive role of the cytopathologist in EUS-FNA. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:485–90. - PubMed
-
- DiMagno EP, Buxton JL, Regan PT, et al. Ultrasonic endoscope. Lancet. 1980;1:629–31. - PubMed
-
- Jhala NC, Jhala DN, Chhieng DC, et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound–Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Cytopathologist's Perspective. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003;120:351–67. - PubMed
-
- Caletti GC, Brocchi E, Ferrari A, et al. Guillotine needle biopsy as a supplement to endosonography in the diagnosis of gastric submucosal tumors. Endoscopy. 1991;23:251–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

