Diagnosis of hydatid cyto-biliary disease by intraductal ultrasound (with video)
- PMID: 24949401
- PMCID: PMC4062277
- DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.121246
Diagnosis of hydatid cyto-biliary disease by intraductal ultrasound (with video)
Abstract
Hydatid disease is one of the relatively common infections in the Middle Eastern countries. It is seen in areas where dogs are used to raise livestock. In humans, the majority of Echinococcus cysts tends to develop in the liver (70%) and is asymptomatic. The two most common complications of hydatid cysts are abscess formation and rupture. Furthermore, in 5-25% of patients, rupture occurs into the biliary tract and patients may present with cholangitis, jaundice, abscess, or bilio-cutaneous fistula after surgery. Intraductal ultrasound (IDUS) is reportedly superior to conventional endoscopic ultrasound for the depiction of bile duct obstruction owing to its additional capability of providing higher resolution images due to the use of higher frequency transducers. Unfortunately IDUS is rarely used, possibly due to the limited availability of appropriate IDUS equipment, cost of the procedure and interventional endoscopists trained in its interpretation. IDUS with wire-guided, thin-caliber, high-frequency probes is a promising imaging modality, yet no previous reports discuss its usefulness in hydatid disease investigation. We hereby present the first report of biliary hydatid disease being diagnosed by IDUS.
Keywords: biliary disease; hydatid disease; intraductal ultrasound.
Figures



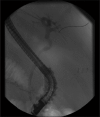
References
-
- Raptou G, Pliakos I, Hytiroglou P, et al. Severe eosinophilic cholangitis with parenchymal destruction of the left hepatic lobe due to hydatid disease. Pathol Int. 2009;59:395–8. - PubMed
-
- Simşek H, Ozaslan E, Sayek I, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP in hepatic hydatid disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:384–9. - PubMed
-
- Smiljanic L, Papic N, Patrlj L, et al. Education and imaging. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic: Biliary rupture of an hydatid cyst. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:431. - PubMed
-
- Khoshbaten M, Farhang S, Hajavi N. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography for intrabiliary rupture of hydatid cyst. Dig Endosc. 2009;21:277–9. - PubMed
-
- Krishna NB, Saripalli S, Safdar R, et al. Intraductal US in evaluation of biliary strictures without a mass lesion on CT scan or magnetic resonance imaging: Significance of focal wall thickening and extrinsic compression at the stricture site. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:90–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

